|
Return to Florasulam
Index Page
Activity:
Herbicide
Structure:
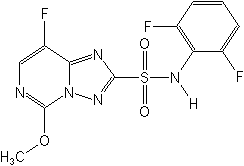
Adverse
Effects:
Anemia
Body Weight Decrease
Endocrine:
Adrenal
Kidney
Liver
Environmental
Anemia
(click on for all
fluorinated pesticides)
Short
term toxicity. Target / critical effect:
Anemia, hepatotoxicity
, renal hypertrophy epithelial cells, collecting ducts,
adrenal vacuolation(dog ) Lowest
relevant oral NOAEL / NOEL: 1 y & 90 d dog (oral feed) ; 5 mg/kg
bw/d;...
Ref: September 18, 2002 - Review report
for the active substance florasulam. European Commission Health
& Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Florasulam.EU.Sept.2002.pdf
Body
Weight Decrease
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- In the rat 90-d
dietary study, other histopathological findings in the kidney
included degeneration with regeneration in the descending portion
of the proximal tubules (females at 500 mg/kg bw/d and above)
which was considered to be typical of acute necrosis with regeneration
rather than a 90-d old lesion and multi-focal mineralization in
the papilla (females at 800 mg/kg bw/d). These lesions did not
appear to be reversible. In the rat 2- year dietary study, other
histopathological findings in the kidneys included a possible
slight decreased incidence of age-related tubular degeneration/regeneration
and a decreased severity of spontaneous geriatric renal degeneration
(chronic progressive glomerularnephropathy) in males at 250 mg/kg
bw/d and above, slight decreased incidence of spontaneous geriatric
renal disease in females at 250 mg/kg bw/d and minimal reactive
hyperplasia of the transitional epithelium and unilateral necrosis
of the papilla in males at 500 mg/kg bw/d. The high-dose males
also exhibited decreased proteinuria, which was considered to
represent less severe chronic renal disease although the decreased
specific gravity suggest that dilution may have also contributed
to lower values. Body weight and body-weight
gain were significantly lower in males at 1000 mg/kg bw/d
and in females at 500 mg/kg bw/d and above in the 90-d dietary
study and in males at 500 mg/kg bw/d (highest dose tested [HDT])
and in females at 250 mg/kg bw/d (HDT) in the 2-year dietary study.
This was associated with concomitant lower food consumption in
the high-dose animals in the both 90-d and 2-year dietary study.
-- In the dog, an increased incidence and
severity of hypertrophy of the epithelial cells was observed in
both sexes at 50 mg/kg bw/d and above in both the 90-d and 1-year
dietary study. There were no treatment-related urinalysis findings
in either the 90-d or 1-year dietary study. The severity (slight)
of the hypertrophy did not appear to increase with prolonged exposure.
In the 90-d dietary study treatment-related findings associated
with the liver included increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity
in both sexes at 50 and 100 mg/kg bw/d, increased liver weights
in both sexes at 100 mg/kg bw/d and a slight increased incidence
or severity of hepatic vacuolation in both sexes at 50 and 100
mg/kg bw/d. Increased liver weights and hepatic vacuolation were
not observed in the 1-year dietary study. In the 1-year dietary
study, treatment-related findings associated with the liver, included
increased alanine aminotransferase (ALAT) and ALP activity and
decreased serum albumin and protein levels in both sexes at 100
mg/kg bw/d. After the high dose was reduced to 50 mg/kg bw/d (week
15), ALP activity remained elevated and serum albumin and protein
levels remained lower in both sexes. In the 1-year dietary study,
no histopathological findings were evident in the liver. In the
1-year dietary study, slight vacuolization of the zona reticularis
and zona fasciculata in the adrenal glands was observed in the
high-dose males and females; however, in the absence of any associated
inflamation, necrosis or other changes, the toxicological significance
of this finding was uncertain. The vacuolization was consistent
with fatty changes. Body weight,
body-weight gain and food consumption were significantly lower
in both sexes at 100 mg/kg bw/d and remained lower in the high-dose
females after the high dose was reduced in the 1-year dietary
study. Body weight, body-weight gain and food consumption were
unaffected by treatment in the 90-d dietary study.
Ref: Florasulam EF-1343 Suspension Concentrate
Herbicide. REF2001-12. September 21, 2001. Canadian Pest Management
Regulatory Agency. Health Canada.
http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/pmra-arla/english/pdf/reg/reg2001-12-e.pdf
Endocrine:
Adrenal
(click on for all fluorinated pesticides)
Short
term toxicity. Target / critical effect:
Anemia, hepatotoxicity , renal hypertrophy epithelial cells, collecting
ducts, adrenal vacuolation(dog )
Lowest relevant oral NOAEL / NOEL: 1 y & 90 d dog (oral feed)
; 5 mg/kg bw/d;...
Ref: September 18, 2002 - Review report
for the active substance florasulam. European Commission Health
& Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Florasulam.EU.Sept.2002.pdf
--
The subchronic and chronic toxicity of florasulam was investigated
in the mouse, rat and dog. A 28-d repeat dose dermal toxicity
study was also carried out in rats. In the subchronic and chronic
studies, treatment-related findings were
observed in the kidney in all species and in the liver
and adrenal glands in dogs. In the
kidney, hypertrophy of the epithelial cells
of the collecting ducts occurred in all species tested.
-- In subchronic and chronic dietary studies, treatment-related
findings were observed in the kidneys in mice, rats and dogs and
in the liver and adrenal glands in the dog.
In the kidney, hypertrophy of the epithelial cells of the collecting
duct was observed in all species tested. In rats, hypertrophy
of the epithelial cells correlated with elevated serum bicarbonate
levels, urinary acidification, decreased urinary specific gravity
and increased kidney weights. In dogs, treatment-related findings
associated with the liver included increased ALP activity, decreased
serum albumin and protein levels, increased liver weights and
increased incidence or severity of hepatic vacuolation.
Dogs also exhibited slight vacuolization of the zona reticularis
and zona fasciculata in the adrenal glands; however, in
the absence of any associated inflammation, necrosis or other
changes, the toxicological significance was uncertain. The most
appropriate NOAEL for subchronic and chronic toxicity end points
is 5.0 mg/kg bw/d in the 90-d and 1-year dietary studies in dogs.
At the LOAEL, 50 mg/kg bw/d, treatment-related findings were observed
in the kidneys and liver in the 90-d and 1-year
dietary studies and in the adrenal glands in the 1-year dietary
study.
Ref: Florasulam EF-1343 Suspension Concentrate
Herbicide. REF2001-12. September 21, 2001. Canadian Pest Management
Regulatory Agency. Health Canada.
http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/pmra-arla/english/pdf/reg/reg2001-12-e.pdf
Kidney
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
-- Short
term toxicity.
Target / critical effect: Anemia, hepatotoxicity , renal
hypertrophy epithelial cells, collecting ducts, adrenal
vacuolation(dog ) Lowest relevant oral NOAEL / NOEL: 1
y & 90 d dog (oral feed) ; 5 mg/kg bw/d;...
-- Long term toxicity and carcinogenicity.
Target / critical effect: kidney collecting
duct hypertrophy, papillary mineralisation, necrosis and inflammation
(rat and/or mice) Lowest relevant NOAEL: 2 yr rat (oral feed):
10 mg/kg bw/d. no carcinogenic potential. Other toxicological
studies Renal cells affected are
probably Type A intercalated cells, involved in acid-base regulation.
Ref: September 18, 2002 - Review report
for the active substance florasulam. European Commission Health
& Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Florasulam.EU.Sept.2002.pdf
-- In the rat 90-d dietary study, other histopathological findings
in the kidney included degeneration
with regeneration in the descending portion of the proximal tubules
(females at 500 mg/kg bw/d and above) which was considered to
be typical of acute necrosis with regeneration rather than a 90-d
old lesion and multi-focal mineralization
in the papilla (females at 800 mg/kg bw/d). These
lesions did not appear to be reversible. In the rat 2-
year dietary study, other histopathological findings in the kidneys
included a possible slight decreased incidence of age-related
tubular degeneration/regeneration and a decreased severity of
spontaneous geriatric renal degeneration (chronic
progressive glomerularnephropathy) in males at 250 mg/kg
bw/d and above, slight decreased incidence of spontaneous geriatric
renal disease in females at 250 mg/kg bw/d and minimal reactive
hyperplasia of the transitional epithelium and unilateral necrosis
of the papilla in males at 500 mg/kg bw/d. The high-dose males
also exhibited decreased proteinuria, which
was considered to represent less severe chronic renal disease
although the decreased specific gravity suggest that dilution
may have also contributed to lower values.
Body weight and body-weight gain were significantly lower in
males at 1000 mg/kg bw/d and in females at 500 mg/kg bw/d and
above in the 90-d dietary study and in males at 500 mg/kg bw/d
(highest dose tested [HDT]) and in females at 250 mg/kg bw/d (HDT)
in the 2-year dietary study. This was associated with concomitant
lower food consumption in the high-dose animals in the both 90-d
and 2-year dietary study.
-- The subchronic and chronic toxicity of florasulam was investigated
in the mouse, rat and dog. A 28-d repeat dose dermal toxicity
study was also carried out in rats. In the subchronic and chronic
studies, treatment-related findings were observed in the kidney
in all species and in the liver and
adrenal glands in dogs. In the kidney,
hypertrophy of the epithelial cells
of the collecting ducts occurred in all species tested.
-- In subchronic and chronic dietary studies, treatment-related
findings were observed in the kidneys in
mice, rats and dogs and in the liver and
adrenal glands in the dog.
In the kidney,
hypertrophy of the epithelial cells of the collecting duct was
observed in all species tested. In rats, hypertrophy of
the epithelial cells correlated with elevated serum bicarbonate
levels, urinary acidification, decreased urinary specific gravity
and increased kidney weights. In
dogs, treatment-related findings associated with the
liver included increased ALP activity, decreased serum
albumin and protein levels, increased liver
weights and increased incidence or severity of hepatic
vacuolation. Dogs also exhibited slight
vacuolization of the zona reticularis and zona fasciculata in
the adrenal glands; however, in the absence of any associated
inflammation, necrosis or other changes, the toxicological significance
was uncertain. The most appropriate NOAEL for subchronic and chronic
toxicity end points is 5.0 mg/kg bw/d in the 90-d and 1-year dietary
studies in dogs. At the LOAEL, 50 mg/kg bw/d, treatment-related
findings were observed in the kidneys
and liver in the 90-d and 1-year dietary studies and in the adrenal
glands in the 1-year dietary study.
Ref: Florasulam EF-1343 Suspension Concentrate
Herbicide. REF2001-12. September 21, 2001. Canadian Pest Management
Regulatory Agency. Health Canada.
http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/pmra-arla/english/pdf/reg/reg2001-12-e.pdf
Liver
(click on for
all fluorinated pesticides)
Short
term toxicity. Target / critical effect:
Anemia, hepatotoxicity , renal hypertrophy
epithelial cells, collecting ducts, adrenal
vacuolation(dog ) Lowest relevant oral NOAEL / NOEL: 1
y & 90 d dog (oral feed) ; 5 mg/kg bw/d;...
Ref: September 18, 2002 - Review report
for the active substance florasulam. European Commission Health
& Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
http://www.fluoridealert.org/pesticides/Florasulam.EU.Sept.2002.pdf
-- The subchronic and
chronic toxicity of florasulam was investigated in the mouse,
rat and dog. A 28-d repeat dose dermal toxicity study was also
carried out in rats. In the subchronic and chronic studies, treatment-related
findings were observed in the kidney in
all species and in the liver and
adrenal glands in dogs.
In the kidney, hypertrophy of the epithelial cells of the collecting
ducts occurred in all species tested.
-- In subchronic and chronic dietary studies, treatment-related
findings were observed in the kidneys in mice, rats and dogs and
in the liver and adrenal glands in the dog. In the kidney, hypertrophy
of the epithelial cells of the collecting duct was observed in
all species tested. In rats, hypertrophy of the epithelial cells
correlated with elevated serum bicarbonate levels, urinary acidification,
decreased urinary specific gravity and increased kidney weights.
In dogs, treatment-related
findings associated with the liver
included increased ALP activity, decreased
serum albumin and protein levels, increased liver weights and
increased incidence or severity of hepatic vacuolation. Dogs also
exhibited slight vacuolization of the zona reticularis and zona
fasciculata in the adrenal glands; however, in the absence of
any associated inflammation, necrosis or other changes,
the toxicological significance was uncertain. The most appropriate
NOAEL for subchronic and chronic toxicity end points is 5.0 mg/kg
bw/d in the 90-d and 1-year dietary studies in dogs. At the LOAEL,
50 mg/kg bw/d, treatment-related findings were observed in the
kidneys and
liver in the
90-d and 1-year dietary studies and in the
adrenal glands in the 1-year dietary study.
-- In the dog, an increased incidence and severity of
hypertrophy of the epithelial cells was observed in both sexes
at 50 mg/kg bw/d and above in both the 90-d and 1-year dietary
study. There were no treatment-related urinalysis findings
in either the 90-d or 1-year dietary study. The severity (slight)
of the hypertrophy did not appear to increase with prolonged exposure.
In the 90-d dietary study treatment-related findings associated
with the liver included increased alkaline
phosphatase (ALP) activity in both sexes
at 50 and 100 mg/kg bw/d, increased liver weights in
both sexes at 100 mg/kg bw/d and a slight increased incidence
or severity of hepatic vacuolation in both
sexes at 50 and 100 mg/kg bw/d.
Increased liver weights and hepatic vacuolation were not observed
in the 1-year dietary study. In the 1-year dietary study, treatment-related
findings associated with the liver,
included increased alanine aminotransferase
(ALAT) and ALP activity and decreased serum albumin and
protein levels in both sexes at 100 mg/kg bw/d. After the high
dose was reduced to 50 mg/kg bw/d (week 15), ALP activity remained
elevated and serum albumin and protein levels remained lower in
both sexes. In the 1-year dietary study, no histopathological
findings were evident in the liver. In the 1-year dietary study,
slight vacuolization of the zona reticularis
and zona fasciculata in the adrenal glands was observed in the
high-dose males and females; however, in the absence of any associated
inflamation, necrosis or other changes, the toxicological significance
of this finding was uncertain. The vacuolization was consistent
with fatty changes. Body weight, body-weight gain and food consumption
were significantly lower in both sexes at 100 mg/kg bw/d
and remained lower in the high-dose females after the high dose
was reduced in the 1-year dietary study. Body weight, body-weight
gain and food consumption were unaffected by treatment in the
90-d dietary study.
-- Ref: Florasulam EF-1343 Suspension Concentrate
Herbicide. REF2001-12. September 21, 2001. Canadian Pest Management
Regulatory Agency. Health Canada.
http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/pmra-arla/english/pdf/reg/reg2001-12-e.pdf
| Environmental
(click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
European
Union:
Only
uses as herbicide may be authorised. For the implementation
of the uniform principles of Annex VI, the conclusions of
the review report on florasulam, and in particular Appendices
I and II thereof, as finalised in the Standing Committee
on the Food Chain and Animal Health on 19 April 2002 shall
be taken into account. In this overall assessment Member
States: Ñ should pay particular attention
to the potential for groundwater contamination, when the
active substance is applied in regions with vulnerable soil
and/or climatic conditions.
Conditions of authorisation must include
risk-mitigation measures, where appropriate.
Ref:
COUNCIL DIRECTIVE of 15 July 1991 concerning the placing
of plant protection products on the market 91/414/EEC -
amended by 2003/5/EC (OJ No. L 8, 14.01.2003, p. 7)
http://www.uksup.sk/download/oso/20030409_smernica_rady_91_414_eec.pdf
|
|

