|
Return
to Tembotrione Index Page
ACTIVITY: Herbicide
CAS Name:
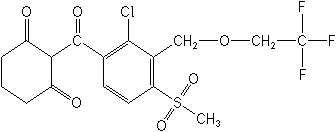
Structure:
Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Brain
Carcinogenicity: EYE
Cholesterol
Endocrine: Ovary
Endocrine: Pancreas
Endocrine: Pituitary
Endocrine: Suspected Disruptor
Endocrine: Testes
Endocrine: Thyroid
Eye
Gallbladder
Kidney
Liver
Sciatic nerve
US EPA APPROVED THE FIRST-TIME USE OF TEMBOTRIONE ON SEPTEMBER 28, 2007.
Tembotrione is a broad spectrum early and mid-postemergence herbicide. It is applied via groundboom equipment at an application rate of 0.082 lb ai/acre. The maximum application rate is 0.16 lb ai/acre (2 applications/season). Tembotrione belongs to the triketone class of herbicides and acts by inhibiting 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) which leads to chlorophyll destruction by photooxidation and causes bleaching of emerging foliar tissue. In mammals, HPPD is a key enzyme in the catabolism of tyrosine. It catalyzes the conversion of 4- hydroxyphenylpyruvate (HPP) to homogentisate. Inhibition of HPPD leads to a reconversion of HPP to tyrosine and a consequent increase in blood tyrosine concentrations (tyrosinemia). There are no existing tolerances, uses, or exemptions for tembotrione. The field corn petition represents the first proposed use for tembotrione. There are currently no proposed residential
uses of tembotrione. This is a joint shared review with PMRA in the U.S. It is currently registered in Austria. Currently, there are three registered herbicides, isoxaflutole [FLUORINATED], topramezone, and mesotrione, and one new herbicide in the review process (pyrasulfatole) [FLUORINATED] that are also HPPD inhibitors. (page 6)
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
|
Blood (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• This non-guideline study (MRID 46695732) [2004] was performed to evaluate the effects of AE 0172747 on blood tyrosine levels in pregnant rabbits following administration by gavage from GD 6-28. AE 0172747(Tembotrione) has been shown to inhibit 4- hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPDase). HPPDase is involved in L-tyrosine catabolism, and inhibition of this enzyme leads to an increase in systemic L-tyrosine concentrations. In this study, AE 0172747 (95.0% a.i.; Bacth # PFI 0195) in aqueous 0.5PFI 0195) in aqueous 0.5% methylcellulose was administered daily via oral gavage at a dose volume of 4 mL/kg to groups of 6 presumed pregnant New Zealand White (KBL [NZW]) rabbits/dose at dose levels of 0 or 10 mg/kg bw/day on gestation days (GD) 6-28. Clinical observations, body weights, and food consumption were recorded at regular intervals during treatment. Blood samples were taken from each animal on GD 4, 10, 15, 22, and 29, and the levels of tyrosine were determined. All surviving does were killed on GD 29 for examination of their uterine contents. Pre-treatment (GD 4) L-tyrosine levels were similar between the treated and control groups. Control group tyrosine levels also remained relatively constant throughout the study (GD 4-29). Animals treated with AE 0172747 displayed marked increases in blood tyrosine levels at all time points examined (39.33-98.93 mg/L) compared to controls (10.00-15.32 mg/L), and the changes in blood tyrosine levels relative to GD 4 were significantly (p≤0.01) higher than controls for all intervals measured during treatment (page 92).
• The dog appeared to be more sensitive to hematological effects. In the subchronic and chronic dog toxicity studies hematological changes indicative of anemia were seen [decreased mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) and mean corpuscular volume (MCV)]. Similar hematological effects were also observed in the chronic toxicity study in the mouse (page 6).
• Chronic/carcinogenicity mouse study. MRID 46695706 (2005). 0, 30, 300, 1000, or 3000 ppm. M: 0, 4, 43, 146, 440 mg/kg/day. F: 0, 5, 54, 179, 552 mg/kg/day. NOAEL was not established. LOAEL =M/F: 4/5 mg/kg/day based on based on gallstones, eosinophilic cytoplasmic alteration, subepithelial mixed cell infiltrate, and dilatation in/of the gallbladder; hepatocellular vacuolation, hepatocellular hypertrophy, and increased liver weight in males and females; and papillary mineralization of the kidney and changes in hematological parameters indicative of anemia in females (page 49).
• Inhibition of 4- Hydroxyphenylpyruvate Dioxygenase in Rats and In Vitro study. MRID 46695733 and 46695734 (2005). In vivo: 0, 10 mg/kg. AE0172747 (Tembotrione) increased plasma tyrosine levels by 20-fold. In vivo: AE1417286 increased plasma tyrosine levels by 5-fold.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
NOTE ON TYROSINE: Tembotrione [FLUORINATED], mesotrione, pyrasulfotole [FLUORINATED], isoxaflutole [FLUORINATED] and topramezone belongs to a class of herbicides that inhibit the liver enzyme HPPD, which is involved in the catabolism (metabolic breakdown) of tyrosine (an amino acid derived from proteins in the diet). Inhibition of HPPD can result in elevated tyrosine levels in the blood, a condition called tyrosinemia (see Note 2 below). HPPD- inhibiting herbicides have been found to cause a number of toxicities in laboratory animal studies including ocular, developmental, liver and kidney effects. Of these toxicities, it is the ocular effect (corneal opacity) that is highly correlated with the elevated blood tyrosine levels. In fact, rats dosed with tyrosine alone show ocular opacities similar to those seen with HPPD inhibitors. Although the other toxicities may be associated with chemically-induced tyrosinemia, other mechanisms may also be involved.
There are marked differences among species in the ocular toxicity associated with inhibition of HPPD. Ocular effects following treatment with HPPD-inhibitor herbicides are seen in the rat, but not in the mouse. Monkeys also seem to be recalcitrant to the ocular toxicity induced by HPPD inhibition. The explanation of this species-specific response in ocular opacity is related to the species differences in the clearance of tyrosine. A metabolic pathway exists to remove tyrosine from the blood that involves a liver enzyme called tyrosine aminotransferase (TAT). In contrast to rats where ocular toxicity is observed following exposure to HPPD-inhibiting
herbicides, mice and humans are unlikely to achieve the levels of plasma tyrosine necessary to produce ocular opacities because the activity of TAT in these species is much greater compared to rats. Thus, humans and mice have a highly effective metabolic process for handling excess tyrosine. (page 37 )
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
NOTE 2: TYROSINEMIA. Elevated blood tyrosine levels are associated with several clinical entities. The term tyrosinemia was first given to a clinical entity based on observations (eg, elevated blood tyrosine levels) that have proven to be common to various disorders, including transient tyrosinemia of the newborn (TTN), hereditary infantile tyrosinemia (tyrosinemia I), Richner-Hanhart syndrome (tyrosinemia II), and tyrosinemia III. In addition, a mysterious entity called tyrosinosis has been described once in the literature. This designation was chosen at a time when specific enzymatic diagnosis was unavailable, leaving a clinical description that has not been duplicated in the 50 years since its publication.
Transient tyrosinemia is believed to result from delayed enzyme maturation in the tyrosine catabolic pathway. This condition is essentially benign and spontaneously disappears with no sequelae. Transient tyrosinemia is not categorized as an inborn error of metabolism because it is not caused by a genetic mutation.
Hereditary infantile tyrosinemia, or tyrosinemia I, is a completely different disease. Patients have a peculiar (cabbagelike) odor, renal tubular dysfunction (Fanconi syndrome), and survival of less than 12 months of life if untreated. Fulminant onset of liver failure occurs in the first few months of life. Some patients have a later onset, usually before age 6 months, with a somewhat protracted course.
For many years, the diagnosis was based on the observation that plasma tyrosine and methionine levels were significantly elevated. Postmortem examination revealed that both the liver and the kidney had a highly unusual pattern of nodular cirrhosis, the histopathologic hallmark of the disease. In the early 1970s, researchers discovered that most severe liver diseases caused such findings regardless of etiology, and, in the late 1970s, the biochemical and enzymatic causes of the disease were reported.
Tyrosinemia II is a disease with a clinical presentation distinctly different from that described above. This presentation includes herpetiform corneal ulcers and hyperkeratotic lesions of the digits, palms, and soles, as well as mental retardation. The biochemical and enzymatic basis for the disease bears no relationship to that of tyrosinemia I, and tyrosinemia II is not discussed further in this article.
Tyrosinemia III is an extremely rare cause of intermittent ataxia, without hepatorenal involvement or skin lesions, and is also not discussed further in this article.
Reference: Tyrosinemia by Karl S. Roth, MD. http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic2339.htm
Body
Weight Decrease
(click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• There was evidence of increased susceptibility following in utero and postnatal exposure in the developmental and 2-generation studies. Fetal effects were increased skeletal variations including delayed ossification and decreased fetal body weight and increased number of runts. These effects were observed at the lowest dose tested (25 mg/kg/day) and at a dose lower than that which caused marginal maternal toxicity (125 mg/kg/day, decreased body-weight gains and food consumption)... (page 16)
• In a developmental toxicity study (MRID 46695647), AE0172747 (95.0% w/w; Batch# PFI 0195) in 0.5% methylcellulose 400 was administered via gavage at a dose volume of 10 mL/kg to 25 Sprague Dawley rats/dose group at dose levels of 0, 25, 125, or 500 mg/kg/day from gestation days (GD) 6-20. On GD 21, all dams were euthanized, and the uterus was removed via cesarean section and its contents examined. Fetuses were examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations, anomalies, and variations. Maternal body-weight gains were decreased (p<=0.05) by 52-92% >=25 mg/kg/day during GD 6-8, and continued to be decreased (p<=0.05) by 28-32% at >=125 mg/kg/day during GD 8-
10. Body-weight gains for the overall (GD 0-21) study were decreased (not significant) by 9% at >=125 25 mg/kg/day; and these decreases were still evident when corrected for gravid uterine weight (decr.11-13%). Food consumption was decreased (p<=0.05) by 8-16% in the 125 and 500 mg/kg/day dams during GD 6-12 and remained decreased (decr.11%; p<=0.01) at 500 mg/kg/day during GD 12-14. Because the decrease in body-weight gain in the 25 mg/kg/day group was transient and did not affect overall body-weight gains, it was not considered adverse. Although not adverse to the dams, this initial decrease in weight gain may have contributed to the decreased (decr.3%; p<=0.01) fetal body weights at this dose. The maternal LOAEL is 125 mg/kg/day based on decreased body-weight gains and food consumption. The maternal NOAEL is 25 mg/kg/day.
-- At >=25 mg/kg/day, fetal body weights were dose-dependently decreased (p<=0.01) by 3-16% and a dose-related increase in the number of runts (fetuses weighing less than 4.0 g) was observed compared to controls.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
• In a developmental toxicity study (MRIDs 46695703, 46695701, and 46695702), AE0172747 (95.0% w/w; Batch# PFI 0195) in 0.5% methylcellulose 400 was administered via gavage at a dose volume of 4 mL/kg to 25 New Zealand White rabbits/dose group at dose levels of 0, 1, 10, or 100 mg/kg bw/day from gestation days (GD) 6-28. On GD 29, all surviving does were euthanized, and the uterus was removed via cesarean section and its contents examined. Fetuses were examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations, anomalies, and variations. At 100 mg/kg bw/day, between GD 15 and 22, five pregnant females were either found dead or were euthanized in extremis or following abortion. Of these five animals, one (#530) was found dead on GD 15; three (#529, 526, and 522) were euthanized in extremis on GD 16, 17, 22; and another (# 517) aborted and was euthanized on GD 21. Marked reductions in food consumption, body-weight loss (between -0.17 and -0.55 kg), and one or more occasions of few or no feces were observed in all five of these does prior to death.. At 10 mg/kg bw/day, one female (# 499) showed a marked reduction in food consumption, body- weight loss of -0.20 kg, and one or more occasions of few or no feces prior to abortion on GD 23. Absolute and relative (to body weight) food consumption were decreased (p≤0.05) by 17% in the 10 mg/kg bw/day group at the beginning of treatment from GD 6-8. At 1 mg/kg bw/day, one female (#475) was killed in extremis on GD 21 following: a marked reduction in food consumption; body-weight loss of -0.35 kg; one or more occasions of few or no feces; and one occasion (GD 19) of no urine.
--
The maternal LOAEL is 100 mg/kg bw/day based on mortality, clinical signs of toxicity (i.e., few or no feces), abortion and decreased body weight and food consumption.
--
The maternal NOAEL is 10 mg/kg bw/day (page 65-66).
-- The developmental LOAEL is 10 mg/kg bw/day based on decreased or delayed growth and/or development of the skeleton and increased incidences of other skeletal variations
and anomalies.
--
The developmental NOAEL is 1 mg/kg bw/day.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Bone (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• In a developmental toxicity study (MRID 46695647), AE0172747 (95.0% w/w; Batch# PFI 0195) in 0.5% methylcellulose 400 was administered via gavage at a dose volume of 10 mL/kg to 25 Sprague Dawley rats/dose group at dose levels of 0, 25, 125, or 500 mg/kg/day from gestation days (GD) 6-20. On GD 21, all dams were euthanized, and the uterus was removed via cesarean section and its contents examined. Fetuses were examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations, anomalies, and variations.
--
At >=25 mg/kg/day, fetal body weights were dose-dependently decreased (p<=0.01) by 3-16% and a dose-related increase in the number of runts (fetuses weighing less than 4.0 g) was observed compared to controls. Additionally at these doses, incidences of the following skeletal variations, indicative of altered growth and development, were increased over controls:
(i) enlarged (poor ossification) of the anterior and/or posterior fontanelle [a fontanelle -or fontanel- is one of two "soft spots" on a newborn human's skull.]
(ii) unossified 7th cervical centrum;
(iii) incomplete ossification of the 5th and/or 6th sternebrae, hemisternebra of the 5th sternebrae, or bipartite 5th sternebrae;
(iv) extra ossification points (unilateral/bilateral) on the 14th thoracic vertebra;
(v) incomplete ossification of the thoracic centrum;
(vi) unossified 3rd and/or 4th proximal phalanges on the forepaws;
(vii) incomplete ossification or unossified 5th metacarpals;
(viii) unossified 1st metatarsals; and
(ix) less than 9 sacrocaudal vertebrae ossified/9 first sacrocaudal vertebrae.
-- Additionally at >=125 mg/kg/day, incidences of the following skeletal variations and anomalies were increased over controls:
(i) bilateral incomplete ossification of the supraoccipital, interparietal, nasals, frontals, and /or parietals;
(ii) unossified 5th and/or 6th sternebrae;
(iii) unossified thoracic centrum; and
(iv) bipartite and/or dumbbell thoracic centrum and cartilage.
-- Finally at 500 mg/kg/day, incidences of the following skeletal variations were increased over controls:
(i) unossified hyoid centrum;
(ii) unossified 7th cervical centrum, cartilage bipartite;
(iii) bipartite ossification, incomplete ossification, or unossified 1st, 2nd, and/or 4th sternebrae.
-- At >=25 25 mg/kg/day, incidences of short unilateral/bilateral 14th thoracic ribs were increased over controls. Additionally at >=125 mg/kg/day, incidences of bipartite and/or dumbbell thoracic centrum and cartilage were increased over controls.
--
At 500 mg/kg/day, incidences of the following variations were increased over controls:
(i) enlarged thymus;
(ii) split, bipartite, or branched xiphoid process;
(iii) bipartite and/or dumbbell thoracic centrum; and
(iv) dumbbell 1st lumbar centrum.
Additionally at this dose, enlarged bladder and absent (unilateral) renal papilla were noted in a single fetus.
-- The developmental LOAEL is 25 mg/kg/day based on increased skeletal variations including delayed ossifications and on decreased growth and development as indicated by decreased fetal body weights, and an increased number of runts.
-- The developmental NOAEL was not observed. (pages 63-65)
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
• In a developmental toxicity study (MRIDs 46695703, 46695701, and 46695702), AE0172747 (95.0% w/w; Batch# PFI 0195) in 0.5% methylcellulose 400 was administered via gavage at a dose volume of 4 mL/kg to 25 New Zealand White rabbits/dose group at dose levels of 0, 1, 10, or 100 mg/kg bw/day from gestation days (GD) 6-28. On GD 29, all surviving does were euthanized, and the uterus was removed via cesarean section and its contents examined. Fetuses were examined for external, visceral, and skeletal malformations, anomalies, and variations...
--
At 10 and 100 mg/kg/day, incidences of the following skeletal variations and anomalies were increased over controls and indicate decreased or delayed growth and development:
(i) enlarged (poor ossification) of the anterior and/or posterior fontanelle;
(ii) unossified atlas centrum;
(iii) extra ossification site between atlas and axis centrum;
(iv) incomplete ossification of the 1st or 2nd sternebra;
(v) unilateral/bilateral incomplete ossification of the pubis;
(vi) unossified 1st or 2nd sternebra; and
(vii) extra sternebral ossification.
--
Additionally at 100 mg/kg/day, the incidence of unossified 6th sternebra was higher than controls.
-- At 10 and 100 mg/kg/day, incidences of the following skeletal variations were increased over concurrent controls:
(i) cartilage of 8th rib (unilateral/bilateral) attached to the sternum;
(ii) cartilage of 1st and 2nd rib (unilateral/bilateral) fused;
(iii) presence of 27 pre-sacral vertebrae; and
(iv) 13 thoracic rib(s) unilateral/bilateral and presence of 27 pre-sacral vertebrae.
-- Additionally at 100 mg/kg/day,
(i) unilateral/bilateral 1st ribs short;
(ii) cartilage of 1st rib (unilateral/bilateral) not attached to the sternum; and
(iii) 14 thoracic ribs (bilateral) or 14 thoracic rib (unilateral) short and/or detached.
-- Additionally at 100 mg/kg/day, incidences of the following visceral variations were increased over concurrent controls:
(i) short innominate arteries;
(ii) absent innominate arteries; and
(iii) dilated cerebral lateral ventricles (bilateral).
-- At 100 mg/kg/day, fused kidneys and retroesophageal aortic arch were noted in a single fetus (each) compared to 0 controls. Incidences of all other malformations were unrelated to dose.
-- The developmental LOAEL is 10 mg/kg bw/day based on decreased or delayed growth and/or development of the skeleton and increased incidences of other skeletal variations and anomalies.
--
The developmental NOAEL is 1 mg/kg bw/day (page 66).
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
• There was evidence of increased susceptibility following in utero and postnatal exposure in the developmental and 2-generation studies. Fetal effects were increased skeletal variations including delayed ossification and decreased fetal body weight and increased number of runts. These effects were observed at the lowest dose tested (25 mg/kg/day) and at a dose lower than that which caused marginal maternal toxicity (125 mg/kg/day, decreased body-weight gains and food consumption). page 16
• In the rabbit developmental study, decreased growth and/or delayed development of the skeleton and increased incidences of skeletal variations and anomalies in fetuses occurred at the a dose (10 mg/kg/day) lower than that which caused maternal toxicity (100 mg/kg/day, few or no feces, late abortion, decreased body weight and food consumption). In the 2-generation reproduction study in rats, parental effects occur at the lowest dose tested (1.4/1.6 mg/kg/day, M/F) and include corneal opacity, acute inflammation and neovascularization of the cornea. Offspring effects occurred at the same dose and included similar eye effects as well as increased incidences of minimal extramedullary hematopoeisis in the spleen, delayed preputial separation, and decreased absolute brain weight. There were no effects on reproduction (page 16).
• In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695708) Wistar male rats/dose in the diet at dose levels of 0, 1, 20, 200 or 800 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.04, 0.79, 8.3 or 31.7 mg/kg bw/day) in the diet for 104 weeks. In the skeletal muscle, the incidence of minimal to moderate atrophy was significantly increased in the 800 ppm group (49%) when compared to controls (32%) (pages 71,73).
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Brain (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- Evidence of neurotoxicity was noted in the subchronic and chronic toxicity studies in the dog and the acute and developmental neurotoxicity studies in the rat (page 20).
-- Rats: decreased absolute brain weight (pp 7, 16, 20, 56, 68, 88).
-- Developmental Neurotoxicity/ Rat study: brain morphometric changes and decreased acoustic startle response were observed in offspring at the lowest dose tested (0.8 mg/kg/day). These effects were observed at a dose lower than that which caused maternal toxicity (16.3 mg/kg/day, corneal opacity). (p 16) ... the brain morphometric changes were presumed to occur following a single exposure (p 21-22).
-- Relative brain weight was significantly (p<0.01) increased in both males and females by 11 and 12% respectively, at 7000 ppm. Absolute brain weight decreased significantly (p<0.001) by 6% in 7000 ppm males only and was comparable to controls in females (p 56).
-- absolute brain weights were dose-dependently decreased (p≤0.05) in both sexes in both generations. In F1 male and female pups, absolute brain weights significantly decreased 3-10% in all treatment groups. In the F2 generation, absolute brain weights significantly decreased 5-9% in males and females at ≥ 200 ppm. Relative brain weights were significantly increased (p≤0.05) in only F1 males and females by 8-9% at ≥200 ppm (p 68).
-- In an acute neurotoxicity study (MRID 46695723), groups of non- fasted, young-adult Wistar rats (12/sex/dose) were given a single oral (gavage; 10 mL/kg) dose of AE 0172747 at doses of 0, 200, 500 or 2000 mg/kg (limit dose) and observed for 14 days. The brain and peripheral nervous system tissues collected from the perfused animals in the control and 2000 mg/kg groups were subjected to histopathological evaluation. Positive control data were not provided; however, data previously reviewed by the Agency have been included in this DER. (p 85)
* [definition of morphometric: (Science: technique) method that involves measurement of shape.]
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
• Dose and Endpoint for Establishing RfD: (page 22)
------ Study Selected: Chronic Toxicity/Carcinogenicity (Feeding)/Rat MRID No.: 46695708
------ The NOAEL of 0.04 mg/kg/day was based on neovascularization and edema of the cornea and snow flake-like corneal opacity, unilateral or bilateral keratitis of the eye, decreased mean body weight and mean body-weight gain, increased total cholesterol, higher ketone levels and lower pH values, higher protein levels, increased kidney weight, kidney to body weight and kidney to brain weight ratios, chronic nephropathy and atrophy of the sciatic nerve observed in the male at 0.79 mg/kg/day (LOAEL).
------ UF(s): An UF of 100 was applied to account for interspecies extrapolation (10X)
------ Comments about Study/Endpoint/UF: This study provided the lowest NOAEL in the database (most sensitive endpoint) and will also provide the most protective limits for human effects.
• Evidence of neurotoxicity was seen in the subchronic and chronic toxicity studies in the dog (uncoordinated movement, disturbance in locomotion) and in the acute (decreased arousal, decreased body temperature, decreased motor and locomotor activities) and developmental neurotoxicity (brain morphometric changes, decreased acoustic startle response) studies in the rat. In the developmental neurotoxicity study in rats, increased susceptibility was observed as fetal neurological effects and occurred at a dose that was lower than the dose at which maternal toxicity occurred (corneal opacity). (page 6-7)
• The decreased accoustic startle response observed in adult rats was statistically significant at the mid and high dose but not at the low dose.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Carcinogenicity (click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
• Long-term dietary administration of tembotrione resulted in an increased incidence of thyroid adenomas and squamous cell carcinomas of the cornea in male rats. Since the incidence of thyroid adenomas was not statistically significant, they were considered unrelated to treatment. The levels of the doses tested were adequate. No tumors were noted in female rats or in male and female mice after long-term dietary administration of tembotrione. The HED CARC (April 11, 2007) classified tembotrione as "Suggestive Evidence of Carcinogenic Potential" by the oral route based on the occurrence of eye tumors in male rats; therefore, the quantification of cancer risk is not required.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Cholesterol (click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
• In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695708) Wistar male rats/dose in the dietat dose levels of 0, 1, 20, 200 or 800 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.04, 0.79, 8.3 or 31.7 mg/kg bw/day) in the diet for 104 weeks. Total cholesterol concentrations were significantly increased (p≤ 0.01) at 200 and 800 ppm (46 and 52%, respectively), compared to controls during the first 18 months of treatment. The increased total cholesterol concentrations observed at 800 ppm during the first 18 months of treatment were still present after 3 months of recovery (43%, p<0.01), compared to controls (page 71).
• A treatment related increase in cholesterol was observed in males in a dose-dependent manner that reached significance at ≥75 ppm [1.25 ppm (14%), 75 ppm (22%, p<0.01), 1500 ppm (32%, p<0.001), 7000 ppm (80%, p<0.001) and increased significantly by 34% (p<0.01) in females at 7000 ppm (page 55).
• Dose and Endpoint for Establishing RfD: (page 22)
------ Study Selected: Chronic Toxicity/Carcinogenicity (Feeding)/Rat MRID No.: 46695708
------ The NOAEL of 0.04 mg/kg/day was based on neovascularization and edema of the cornea and snow flake-like corneal opacity, unilateral or bilateral keratitis of the eye, decreased mean body weight and mean body-weight gain, increased total cholesterol, higher ketone levels and lower pH values, higher protein levels, increased kidney weight, kidney to body weight and kidney to brain weight ratios, chronic nephropathy and atrophy of the sciatic nerve observed in the male at 0.79 mg/kg/day (LOAEL).
------ UF(s): An UF of 100 was applied to account for interspecies extrapolation (10X)
------ Comments about Study/Endpoint/UF: This study provided the lowest NOAEL in the database (most sensitive endpoint) and will also provide the most protective limits for human effects.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Endocrine: Ovary (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• 90-day Oral Yoxicity - Mouse study: NOAEL =M/F: 64/75.6 mg/kg/day. LOAEL =M/F: 631/783 mg/kg/day based on decreased uterine weights and increased corpora lutea in the ovary in females... (page 47)
• 90-Day Oral Toxicity - Rat study : In females, the following microscopic changes were observed at an increased incidence: multifocal corticotubular basal vacuolation (slight) in the kidneys occurred in a dose-dependent manner 1-6/10 in all treated groups compared to 0/10 in controls; diffuse hypertrophy of the interstitial gland in the ovaries was observed in the 1500 ppm and 7000 ppm groups (3/10) compared to 0/10 in controls. These effects were considered treatment-related. (page 56)
• Certain changes in multiple organs seen in the subchronic, chronic, dermal, and reproduction studies (e.g., microscopic changes in the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas; increased number of corpora lutea in the ovary, and delayed preputial separation) may be due to various mechanisms including possible liver-pituitary-thyroid homeostatic disruption or inhibition of steroid synthesis (Page 6)... When additional appropriate screening and/or testing protocols being considered under the Agency’s EDSP have been developed, tembotrione may be subjected to further screening and/or testing to better characterize effects related to endocrine disruption (page 29).
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Endocrine: Pancreas (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• Certain changes in multiple organs seen in the subchronic, chronic, dermal, and reproduction studies (e.g., microscopic changes in the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas; increased number of corpora lutea in the ovary, and delayed preputial separation) may be due to various mechanisms including possible liver-pituitary-thyroid homeostatic disruption or inhibition of steroid synthesis (Page 6)... When additional appropriate screening and/or testing protocols being considered under the Agency’s EDSP have been developed, tembotrione may be subjected to further screening and/or testing to better characterize effects related to endocrine disruption (page 29).
• Thyroid gland toxicity was observed in the 21/28-day dermal toxicity study in the rat and chronic oral toxicity study in the dog. Dermal exposure (21/28-day study) resulted in colloid alteration and hypertrophic follicular epithelium in the thyroid gland in the rat. Also observed were degenerative changes in the pancreas, increased proteinacious material in the Ratche pouch in the pituitary gland and basophilic tubules in the kidneys. Pigmentation of the thyroid gland along with hematological changes and microscopic changes in the sciatic nerve were observed in the dog.
• In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695708) Wistar male rats/dose in the diet at dose levels of 0, 1, 20, 200 or 800 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.04, 0.79, 8.3 or 31.7 mg/kg bw/day) in the diet for 104 weeks. In the pancreas, the incidence of minimal to moderate acinar atrophy/fibrosis was significantly increased (p≤0.01) in the 200 and 800 ppm groups (63% and 67%, respectively), when compared to controls (35%). Pancreatic acinar atrophy/fibrosis generally is a focal or lobular atrophy (dedifferentiation of acinar cells and an increase in small duct-like structures), sometimes associated with a relative increase in interstitial collagen and a small number of inflammatory cells, but in the 200 and 800 ppm dose groups this lesion was more diffuse in distribution (page 73).
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Endocrine: Pituitary (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• Certain changes in multiple organs seen in the subchronic, chronic, dermal, and reproduction studies (e.g., microscopic changes in the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas; increased number of corpora lutea in the ovary, and delayed preputial separation) may be due to various mechanisms including possible liver-pituitary-thyroid homeostatic disruption or inhibition of steroid synthesis (Page 6)... When additional appropriate screening and/or testing protocols being considered under the Agency’s EDSP have been developed, tembotrione may be subjected to further screening and/or testing to better characterize effects related to endocrine disruption (page 29).
• In the 2-generation reproduction study in rats, offspring effects. Treatment-related decreases (p≤0.05) in pup body weights were observed: in the F1 pups at 200 and 1500 ppm beginning on PND 7 and continuing throughout the reminder of the post-natal period; and in the F2 pups at 200 ppm beginning on PND 21 and at 1500 ppm beginning on PND 14. Body-weight gains in these groups were dose-dependently decreased. Compared to controls, the time until preputial separation was dose-dependently delayed in all treated groups in the F1 and F2 offspring. This effect was considered treatment related. Also, the time to vaginal opening was longer in the 1500 ppm F1 offspring (page 68).
• In the 2-generation reproduction study in rats, offspring effects. The LOAEL for offspring toxicity is 20 ppm (equivalent to 1.4/1.6 mg/kg/day in males/females) based on effects on the eyes, including corneal opacity, acute inflammation, and neovascularization; increased incidences of minimal extramedullary hematopoeisis in the spleen, delayed preputial separation, and decreased absolute brain weight. The NOAEL was not observed (page 68).
• In a carcinogenicity study with mice (MRID 46695706), AE 0172747 (95% w/w a.i.; Batch No. PFI 0195) was administered in the diet to C57BL/6 J@ Ico mice (50/sex/dose) at doses of 0, 30, 300, 1000, or 3000 ppm (equivalent to 0/0, 4/5, 43/54, 146/179, and 440/552 mg/kg/day in males/females) for up to 78 weeks. Additionally, 10 mice/sex/dose were treatedsimilarly for up to 52 weeks. At 1000 ppm and above at 18 months, the incidences of the following lesions were increased in males:
(i) minimal to marked epithelial hyperplasia (multifocal/diffuse) in the gallbladder;
(ii) minimal to marked focal tubular degeneration (bilateral) in the testes; and
(iii) minimal to slight interstitial cell hyperplasia (focal/multifocal) in testes. Increased incidences of dilatation of uterine horns were noted grossly at ≥1000 ppm.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
• Thyroid gland toxicity was observed in the 21/28-day dermal toxicity study in the rat and chronic oral toxicity study in the dog. Dermal exposure (21/28-day study) resulted in colloid alteration and hypertrophic follicular epithelium in the thyroid gland in the rat. Also observed were degenerative changes in the pancreas, increased proteinacious material in the Ratche pouch in the pituitary gland and basophilic tubules in the kidneys. Pigmentation of the thyroid gland along with hematological changes and microscopic changes in the sciatic nerve were observed in the dog.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Endocrine: Suspected Endocrine Disruptor (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• Certain changes in multiple organs seen in the subchronic, chronic, dermal, and reproduction studies (e.g., microscopic changes in the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas; increased number of corpora lutea in the ovary, and delayed preputial separation) may be due to various mechanisms including possible liver-pituitary-thyroid homeostatic disruption or inhibition of steroid synthesis (page 6).
• When additional appropriate screening and/or testing protocols being considered under the Agency’s EDSP have been developed, tembotrione may be subjected to further screening and/or testing to better characterize effects related to endocrine disruption.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Endocrine: Testes (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• Certain changes in multiple organs seen in the subchronic, chronic, dermal, and reproduction studies (e.g., microscopic changes in the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas; increased number of corpora lutea in the ovary, and delayed preputial separation) may be due to various mechanisms including possible liver-pituitary-thyroid homeostatic disruption or inhibition of steroid synthesis (Page 6)... When additional appropriate screening and/or testing protocols being considered under the Agency’s EDSP have been developed, tembotrione may be subjected to further screening and/or testing to better characterize effects related to endocrine disruption (page 29).
• In the 2-generation reproduction study in rats, offspring effects. Treatment-related decreases (p≤0.05) in pup body weights were observed: in the F1 pups at 200 and 1500 ppm beginning on PND 7 and continuing throughout the reminder of the post-natal period; and in the F2 pups at 200 ppm beginning on PND 21 and at 1500 ppm beginning on PND 14. Body-weight gains in these groups were dose-dependently decreased. Compared to controls, the time until preputial separation was dose-dependently delayed in all treated groups in the F1 and F2 offspring. This effect was considered treatment related. Also, the time to vaginal opening was longer in the 1500 ppm F1 offspring (page 68).
• In the 2-generation reproduction study in rats, offspring effects. The LOAEL for offspring toxicity is 20 ppm (equivalent to 1.4/1.6 mg/kg/day in males/females) based on effects on the eyes, including corneal opacity, acute inflammation, and neovascularization; increased incidences of minimal extramedullary hematopoeisis in the spleen, delayed preputial separation, and decreased absolute brain weight. The NOAEL was not observed (page 68).
• In a carcinogenicity study with mice (MRID 46695706), AE 0172747 (95% w/w a.i.; Batch No. PFI 0195) was administered in the diet to C57BL/6 J@ Ico mice (50/sex/dose) at doses of 0, 30, 300, 1000, or 3000 ppm (equivalent to 0/0, 4/5, 43/54, 146/179, and 440/552 mg/kg/day in males/females) for up to 78 weeks. Additionally, 10 mice/sex/dose were treatedsimilarly for up to 52 weeks. At 1000 ppm and above at 18 months, the incidences of the following lesions were increased in males:
(i) minimal to marked epithelial hyperplasia (multifocal/diffuse) in the gallbladder;
(ii) minimal to marked focal tubular degeneration (bilateral) in the testes; and
(iii) minimal to slight interstitial cell hyperplasia (focal/multifocal) in testes. Increased incidences of dilatation of uterine horns were noted grossly at ≥1000 ppm.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Endocrine: Thyroid (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
-- In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study, squamous cell carcinomas of the cornea and thyroid follicular adenomas were observed in male rats. (page 6)
-- Thyroid gland toxicity was observed in the 21/28-day dermal toxicity study in the rat and chronic oral toxicity study in the dog. Dermal exposure (21/28-day study) resulted in colloid alteration and hypertrophic follicular epithelium in the thyroid gland in the rat. Also observed were degenerative changes in the pancreas, increased proteinacious material in the Ratche pouch in the pituitary gland and basophilic tubules in the kidneys. Pigmentation of the thyroid gland along with hematological changes and microscopic changes in the sciatic nerve were observed in the dog.
• Certain changes in multiple organs seen in the subchronic, chronic, dermal, and reproduction studies (e.g., microscopic changes in the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas; increased number of corpora lutea in the ovary, and delayed preputial separation) may be due to various mechanisms including possible liver-pituitary-thyroid homeostatic disruption or inhibition of steroid synthesis (Page 6)... When additional appropriate screening and/or testing protocols being considered under the Agency’s EDSP have been developed, tembotrione may be subjected to further screening and/or testing to better characterize effects related to endocrine disruption (page 29).
• In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695708) Wistar male rats/dose in the diet at dose levels of 0, 1, 20, 200 or 800 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.04, 0.79, 8.3 or 31.7 mg/kg bw/day) in the diet for 104 weeks. In the thyroid gland, the incidence of minimal to marked pigmentation of the cytoplasm of the follicular epithelial cells was significantly increased (p≤0.01) in the 1, 20, 200, and 800 ppm groups (36%, 66%, 77% and 73%, respectively), when compared to controls (12%). Special stains conducted on two-year males (positive for Schmorl and PAS, minimally positive for Fontana-Masson and negative for Perls) were compatible with lipofuscin pigments. Minimal to slight colloid alteration of the thyroid gland was significantly (p≤0.05) increased in the 20, 200 and 800 ppm groups (63%, 62% and 63%, respectively) when compared to controls (55%). Colloid alteration of the thyroid gland was described as an irregular uniformity of the colloid with differences in staining and globule formation. The severity grade for colloid alteration was increased in the 200 and 800 ppm dose groups. Minimal to mark cystic hyperplasia of the thyroid gland was significantly (p≤0.01) increased in the 200 and 800 ppm groups (13% and 12%, respectively) when compared to controls (0%) (pages 71-73).
• Long-term dietary administration of tembotrione resulted in an increased incidence of thyroid adenomas and squamous cell carcinomas of the cornea in male rats. Since the incidence of thyroid adenomas was not statistically significant, they were considered unrelated to treatment. The levels of the doses tested were adequate. No tumors were noted in female rats or in male and female mice after long-term dietary administration of tembotrione. The HED CARC (April 11, 2007) classified tembotrione as "Suggestive Evidence of Carcinogenic Potential" by the oral route based on the occurrence of eye tumors in male rats; therefore, the quantification of cancer risk is not required.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Eye (click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
• Long-term dietary administration of tembotrione resulted in an increased incidence of thyroid adenomas and squamous cell carcinomas of the cornea in male rats. Since the incidence of thyroid adenomas was not statistically significant, they were considered unrelated to treatment. The levels of the doses tested were adequate. No tumors were noted in female rats or in male and female mice after long-term dietary administration of tembotrione. The HED CARC (April 11, 2007) classified tembotrione as "Suggestive Evidence of Carcinogenic Potential" by the oral route based on the occurrence of eye tumors in male rats; therefore, the quantification of cancer risk is not required.
• The eye, liver and kidney are the primary target organs of tembotrione. In the subchronic, chronic and reproduction rat studies, and the subchronic dog study, corneal opacity, edema of the cornea, neovascularization, and keratitis were seen at various doses indicating ocular toxicity. Males appear to be more susceptible to ocular toxicity than females. Also, corneal opacity was completely reversible following subchronic and chronic exposures in rats and some neovascularizations were reversible following subchronic exposure in rats; but these effects were not reversible following chronic exposure (page 15).
• In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695708)
AE 0172747 was administered to 60 Rj: WI (IOPS HAN) Wistar male rats/dose in the diet at dose levels of 0, 1, 20, 200 or 800 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.04, 0.79, 8.3 or 31.7 mg/kg bw/day) in the diet for 104 weeks. Gross necropsy revealed a higher incidence of ocular opacity at 20, 200, and 800 ppm. The incidence of minimal to marked keratitis of the eye(s) was significantly increased (p≤0.01) in males in the 20, 200, and 800 ppm groups (97-98%) when compared to controls (3%). Keratitis included one or more of the following changes in the cornea: acute inflammation, epithelial hyperplasia, keratinization, epithelial vacuolization, erosion and/or ulceration. Generally, the keratitis observed in this study was a multifocal to diffuse chronic active superficial keratitis, involving the corneal epithelium and superficial aspects of the corneal stroma, which did not penetrate the cornea. A slight non-statistically significant elevation (3-5%) of hyperplastic lesions was noted on the cornea of the eye at 200 and 800 ppm, when compared to controls (0 %). In addition, a minimal to moderate retinal degeneration, mostly located in the ora serrata area of the retina, was significantly increased (p≤0.05) in the 800 ppm group (15%) when compared to controls (3%) (page 79-80).
• Dose and Endpoint for Establishing RfD: (page 22)
-- Study Selected: Chronic Toxicity/Carcinogenicity (Feeding)/Rat MRID No.: 46695708
-- The NOAEL of 0.04 mg/kg/day was based on neovascularization and edema of the cornea and snow flake-like corneal opacity, unilateral or bilateral keratitis of the eye, decreased mean body weight and mean body-weight gain, increased total cholesterol, higher ketone levels and lower pH values, higher protein levels, increased kidney weight, kidney to body weight and kidney to brain weight ratios, chronic nephropathy and atrophy of the sciatic nerve observed in the male at 0.79 mg/kg/day (LOAEL).
--
UF(s): An UF of 100 was applied to account for interspecies extrapolation (10
-- Comments about Study/Endpoint/UF: This study provided the lowest NOAEL in the database (most sensitive endpoint) and will also provide the most protective limits for human effects.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Gallbladder (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
* In a carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695706), AE 0172747 was administered in the diet to C57BL/6 J@ Ico mice (50/sex/dose) at doses of 0, 30, 300, 1000, or 3000 ppm (equivalent to 0/0, 4/5, 43/54, 146/179, and 440/552 mg/kg/day in males/females) for up to 78 weeks. Additionally, 10 mice/sex/dose were treated similarly for up to 52 weeks. At 30 ppm (the lowest dose tested), there was evidence of toxicity in the gallbladder and liver in both sexes. The toxicity became more severe at higher doses. In all treatment groups at 12 months, incidences (n=10) of the following lesions were increased in the gallbladder and liver:
(i) minimal to moderate gallstones in males and females (2-5 treated vs 1 control);
(ii) minimal to marked gallstones in females (2-7 treated vs 0 controls); and
(iii) minimal to moderate centrilobular to panlobular hepatocellular hypertrophy (diffuse) in females (5-10 treated vs 0 controls).
In all treatment groups at 18 months, gallbladder stones were observed in mice at necropsy in both sexes (18-36/50 treated vs 1/50 controls). Incidences of the following microscopic lesions were increased in all treatment groups in the gallbladder (# affected/50 treated vs # affected/50 controls, except n=49 in male controls and 1000 ppm females):
(i) minimal to marked gallstones in both sexes (6-26 vs 0-1; p<=0.001);
(ii) minimal to marked eosinophilic cytoplasmic alteration (focal/multifocal) in females (9-28 vs 2; p<=0.05); and
(iii) minimal to moderate subepithelial mixed cell infiltrate (focal/multifocal) in females (15-29 vs 11; not statistically significant) (pages 73-74).
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Kidney (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• The primary target organs were the eyes, liver and kidneys. In the kidney, increased weight, and papillary mineralization were observed in the rat and mouse following chronic exposure (page 6).
• 90-Day Oral Toxicity - Rat study : In females, the following microscopic changes were observed at an increased incidence: multifocal corticotubular basal vacuolation (slight) in the kidneys occurred in a dose-dependent manner 1-6/10 in all treated groups compared to 0/10 in controls; diffuse hypertrophy of the interstitial gland in the ovaries was observed in the 1500 ppm and 7000 ppm groups (3/10) compared to 0/10 in controls. These effects were considered treatment-related (page 56).
• In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695708) Wistar male rats/dose in the dietat dose levels of 0, 1, 20, 200 or 800 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.04, 0.79, 8.3 or 31.7 mg/kg bw/day) in the diet for 104 weeks. In the kidney, a minimal to severe chronic nephropathy was significantly increased (p≤0.01) in the 20, 200, and 800 ppm group, (87%, 87%, 92%, and 83%, respectively) compared to in the control group (63%). Changes within the kidney included one or more of the following changes: tubular cell regeneration, thickened basement membranes (glomerular and tubular), interstitial fibrosis, inflammation, dilated/cystic tubules, protein casts, pigmentation, mineralization, debris, mesangial proliferation, glomerular sclerosis, and hypertrophy/hyperplasia of tubular epithelium. Severity grades moderate or higher generally reflected a kidney with most of the above- mentioned changes, some reflecting end-stage renal disease (probable cause of death) (page 72).
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
• Dose and Endpoint for Establishing RfD: (page 22)
------ Study Selected: Chronic Toxicity/Carcinogenicity (Feeding)/Rat MRID No.: 46695708
------ The NOAEL of 0.04 mg/kg/day was based on neovascularization and edema of the cornea and snow flake-like corneal opacity, unilateral or bilateral keratitis of the eye, decreased mean body weight and mean body-weight gain, increased total cholesterol, higher ketone levels and lower pH values, higher protein levels, increased kidney weight, kidney to body weight and kidney to brain weight ratios, chronic nephropathy and atrophy of the sciatic nerve observed in the male at 0.79 mg/kg/day (LOAEL).
------ UF(s): An UF of 100 was applied to account for interspecies extrapolation (10X)
------ Comments about Study/Endpoint/UF: This study provided the lowest NOAEL in the database (most sensitive endpoint) and will also provide the most protective limits for human effects.
• Thyroid gland toxicity was observed in the 21/28-day dermal toxicity study in the rat and chronic oral toxicity study in the dog. Dermal exposure (21/28-day study) resulted in colloid alteration and hypertrophic follicular epithelium in the thyroid gland in the rat. Also observed were degenerative changes in the pancreas, increased proteinacious material in the Ratche pouch in the pituitary gland and basophilic tubules in the kidneys. Pigmentation of the thyroid gland along with hematological changes and microscopic changes in the sciatic nerve were observed in the dog.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Liver (click on for all fluorinated
pesticides)
• The primary target organs were the eyes, liver and kidneys. In subchronic and chronic oral toxicity studies- Liver effects (increased weight, hypertrophy, hyperplasia) were seen in the rat, mouse and dog (page 6). In the kidney, increased weight, and papillary mineralization were observed in the rat and mouse following chronic exposure.
• Certain changes in multiple organs seen in the subchronic, chronic, dermal, and reproduction studies (e.g., microscopic changes in the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas; increased number of corpora lutea in the ovary, and delayed preputial separation) may be due to various mechanisms including possible liver-pituitary-thyroid homeostatic disruption or inhibition of steroid synthesis (page 6).
• Chronic/carcinogenicity mouse study. MRID 46695706 (2005). 0, 30, 300, 1000, or 3000 ppm. M: 0, 4, 43, 146, 440 mg/kg/day. F: 0, 5, 54, 179, 552 mg/kg/day. NOAEL was not established. LOAEL =M/F: 4/5 mg/kg/day based on based on gallstones, eosinophilic cytoplasmic alteration, subepithelial mixed cell infiltrate, and dilatation in/of the gallbladder; hepatocellular vacuolation, hepatocellular hypertrophy, and increased liver weight in males and females; and papillary mineralization of the kidney and changes in hematological parameters indicative of anemia in females (page 49).
• In a carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695706), AE 0172747 was administered in the diet to C57BL/6 J@ Ico mice (50/sex/dose) at doses of 0, 30, 300, 1000, or 3000 ppm (equivalent to 0/0, 4/5, 43/54, 146/179, and 440/552 mg/kg/day in males/females) for up to 78 weeks. Additionally, 10 mice/sex/dose were treated similarly for up to 52 weeks. At 30 ppm (the lowest dose tested), there was evidence of toxicity in the gallbladder and liver in both sexes. The toxicity became more severe at higher doses. In all treatment groups at 12 months, incidences (n=10) of the following lesions were increased in the gallbladder and liver:
(iii) minimal to moderate centrilobular to panlobular hepatocellular hypertrophy (diffuse) in females (5-10 treated vs 0 controls). (pages 73-74).
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
Sciatic nerve (click
on for all fluorinated pesticides)
• In a combined chronic/carcinogenicity study (MRID 46695708) Wistar male rats/dose in the diet at dose levels of 0, 1, 20, 200 or 800 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.04, 0.79, 8.3 or 31.7 mg/kg bw/day) in the diet for 104 weeks. In the sciatic nerve, minimal to slight nerve fiber degeneration was significantly increased (p≤0.05) in the 20, 200 and 800 ppm groups (73%, 73% and 75%, respectively), when compared to controls (53%). This change was described as multiple fiber degeneration, loss of stain intensity, decreased density and definition of the nerve fiber and/or demyelination. In addition, sometimes associated with sciatic nerve atrophy was a minimal to moderate chronic inflammatory response and/or minimal to moderate mineralization of the vessels within the nerve. In general, these changes were noted in animals that survived to the terminal sacrifice, indicating a late onset of the exacerbation of this lesion (page 71-72).
• Thyroid gland toxicity was observed in the 21/28-day dermal toxicity study in the rat and chronic oral toxicity study in the dog. Dermal exposure (21/28-day study) resulted in colloid alteration and hypertrophic follicular epithelium in the thyroid gland in the rat. Also observed were degenerative changes in the pancreas, increased proteinacious material in the Ratche pouch in the pituitary gland and basophilic tubules in the kidneys. Pigmentation of the thyroid gland along with hematological changes and microscopic changes in the sciatic nerve were observed in the dog.
• Dose and Endpoint for Establishing RfD: (page 22)
------ Study Selected: Chronic Toxicity/Carcinogenicity (Feeding)/Rat MRID No.: 46695708
------ The NOAEL of 0.04 mg/kg/day was based on neovascularization and edema of the cornea and snow flake-like corneal opacity, unilateral or bilateral keratitis of the eye, decreased mean body weight and mean body-weight gain, increased total cholesterol, higher ketone levels and lower pH values, higher protein levels, increased kidney weight, kidney to body weight and kidney to brain weight ratios, chronic nephropathy and atrophy of the sciatic nerve observed in the male at 0.79 mg/kg/day (LOAEL).
------ UF(s): An UF of 100 was applied to account for interspecies extrapolation (10X)
------ Comments about Study/Endpoint/UF: This study provided the lowest NOAEL in the database (most sensitive endpoint) and will also provide the most protective limits for human effects.
Reference: Tembotrione. Human-Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Uses on Field Corn, Sweet Corn and Popcorn. USEPA. September 7, 2007.
|

