|
Return to
Index Page
Adverse Effects
Abstracts
ACTIVITY: Fungicide
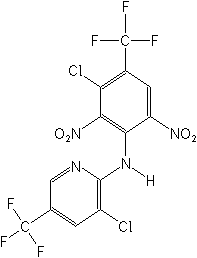
(2,6-Dinitroaniline)
CAS Name: 3-chloro-N-[3-chloro-2,6-dinitro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinamine
Structure:
| |
| Date
Published |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| October 24, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0234 |
IR-4 and ISK Biosciences. Pesticide tolerance. FINAL RULE for PP 6E7137. Documents available in the docket are:
• Fluazinam: Human Health Risk Assessment for Proposed Use on Edible-Podded beams. Shelled and Succulent and Dried Beans, Bassica Lafy Vegetables, Bushberriews, and Gingseng. August 22,2007. EPA Office of Pesticides. Docket No. EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0234-0004.
• Fluazinam Acute and Chronic Aggregate Dietary (Food and Drinking Water) Exposure and Risk Assessments for the Secion 3 Registration Action on Gingseng, Brassica Vegetables, Legume Vegetables, and Bushberries. August 1, 2007. US EPA Office of Pesticides. Docket No. EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0234-0005.
• Tier I Estimated Drinking Waters Concentrations of Fluazinam and Total Residues for the Use in the Human Health Risk Assessment; IR4 Petition for the Use of Fluazinam on Edible-Podded Legume Vegetables (except peas), Bushberry (crop subgroup 13B), Brassica (Cole) Leafy Vegetables, Ginseng, and Dry, and Succulent Bean Crop Subgroup 6B (except peas) 10/24/2007. February 7, 2007. Docket No. EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0234-0007.
• Fluazinam. Tolerance Petitions Requesting the Establishment of Permanent Tolerances (Associated with Section 3 Registration) for Food Use of the Herbicide on Edible-Podded Beans (Subgroup 6-A, Except Peas), Shelled Succulent Beans (Subgroup 6-B, Except Peas), Shelled Dried Beans (Subgroup 6-C, Except Peas), Brassica (Cole) Vegetables (Group 5), Bushberries (Subgroup 13-B), and Ginseng. Summary of Analytical Chemistry and Residue Data. August 22, 2007. US EPA Office of Pesticides. Docket No. EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0234-0006.
• Fluazinam: Company Notice of Filing. January 1, 2006. Docket No. EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0234-0002.
| Commodity |
PPM
FINAL RULE: |
PPM:
PETITIONED: |
EPA's rationale for increasing tolerance: |
Aronia berry
|
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
Buffalo currant
|
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
Bushberry subgroup 13B. This subgroup includes 5 commodities:
blueberry • currant • elderberry •
gooseberry • huckleberry
|
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Chilean guava |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| European barberry |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Ginseng |
4.5 |
3.0 |
Note 5 |
| Highbush cranberry |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Honeysuckle, edible |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Jostaberry |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Juneberry |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Lingonberry |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Native currant |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
Pea and bean, dried shelled, except soybean, subgroup 6C, except pea. This subgroup includes 27 commodities.
bean, adzuki • bean, broad dry • bean, dry • bean, kidney • bean, lablab • bean, lima dry • bean, moth • bean, mung • bean, navy • bean, pink • bean, pinto • bean, rice • bean, tepary • bean, urd • catjang • chickpea • cowpea • guar • lentil • lupin, grain • lupin, sweet • pea, blackeyed • pea, crowder • pea, field • pea, field seed • pea, pigeon • pea, southern
|
0.02 |
0.01 |
Note 2 |
Pea and bean, succulent shelled, subgroup 6B, except pea. This subgroup includes 10 commodities:
bean, broad succulent • bean, lima succulent
• cowpea • cowpea seed • pea, blackeyed
• pea, english • pea, garden • pea,
green • pea, pigeon • pea, southern
|
0.04 |
0.02 |
Note 2 |
| Salal |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Sea buckthorn |
7.0 |
4.5 |
Note 1 |
| Turnip, greens |
0.01 |
0.02 |
Note 4 |
Vegetable, Brassica leafy, group 5. This group includes 16 commodities.
broccoli • broccoli raab • broccoli, chinese • brussels sprouts • cabbage • cabbage, chinese, bok choy • cabbage, chinese, mustard • cabbage, chinese, napa • cauliflower • collards • kale • kohlrabi • mustard greens • mustard spinach • rape greens • vegetable, brassica, leafy, group
|
0.01 |
0.02 |
Note 4 |
Vegetable, legume, edible-podded, subgroup 6A, except pea. This subgroup includes14 commodities.
bean, moth • bean, runner • bean, snap • bean, wax • bean, yardlong • jackbean • longbean, chinese • pea, dwarf • pea, edible podded • pea, pigeon • pea, snow • pea, sugar snap • soybean immature seed • swordbean
|
0.10 |
0.15 |
Note 3 |
Note 1: The tolerances for Bushberry subgroup 13B and related berries were increased from 4.5 ppm to 7.0 ppm based on analyses of the residue field trial data using the Agency's Tolerance Spreadsheet in accordance with the Agency's Guidance for Setting Pesticide Tolerances Based on Field Trial Data. Although IR-4 proposed tolerances for combined residues of fluazinam and AMGT on these commodities, EPA determined, based on the low levels of AMGT seen in the field trials, that only parent fluazinam should be included in the tolerance expression.
Note 2: The commodity terms for dry beans and succulent shelled legumes were revised to read ``Pea and bean, dried shelled, except soybean, subgroup 6C, except pea'' and ``Pea and bean, succulent shelled, subgroup 6B, except pea'' to agree with recommended commodity terms in the Office of Pesticide Program's Food and Feed Commodity Vocabulary. Tolerances for these commodities were increased from 0.01 ppm to 0.02 ppm (dried) and from 0.02 ppm to 0.04 ppm (succulent) to account for the 50% dissipation of residues observed in the storage stability study.
Note 3: The commodity term for edible-podded legume vegetables was revised to read ``Vegetable, legume, edible-podded, subgroup 6A, except pea'' to agree with the Food and Feed Commodity Vocabulary. The tolerance level was decreased from 0.15 ppm to 0.10 ppm based on maximum residues seen in the field trials, since 80% of the residues were non-detectable and, therefore, not appropriate for analysis using the Tolerance Spreadsheet.
Note 4: IR-4 proposed separate tolerances of 0.02 ppm and 0.01 ppm for ``Leafy Brassica greens subgroup'' and ``Head and stem Brassica subgroup'', respectively. EPA determined that a single tolerance of 0.01 ppm covering the entire crop group ``Vegetable, Brassica leafy, group 5'' would be appropriate, based on the results of field trials showing no residues above the method limit of quantitation (LOQ) in any of the representative commodities (broccoli, cabbage and mustard greens). The tolerance for turnip greens was revised from 0.02 to 0.01 ppm on the same basis.
Note 5: The tolerance for ginseng was increased from 3.00 ppm to 4.5 ppm to account for dissipation of residues observed in the storage stability study.
Cancer. In accordance with the 2005 Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment, for fluazinam there is ``Suggestive evidence of carcinogenic potential.'' This determination is based on weight of evidence considerations where a concern for potential carcinogenic effects in humans is raised, but the animal data are judged not sufficient for a stronger conclusion. Carcinogenicity studies were conducted in rats and mice . In mice, there were conflicting results with regard to hepatocarcinogenicity. In the second study, carcinogenic response was equivocal and tumors did not occur in a dose-related manner. In males, the dose that induced liver tumors in the first study failed to induce liver tumors in the same strain of mice in the second study. In the second study, in females, liver tumors were seen only at an excessive toxic dose. There was no evidence of mutagenicity either in in vivo or in vitro assays. No chemicals structurally related to fluazinam were identified as carcinogens. Since the evidence for carcinogenicity is not sufficient to indicate anything greater than a suggestion of a carcinogenic potential, EPA concludes that quantification of cancer risk would not be scientifically appropriate, as it attaches greater significance to the positive cancer findings than the entire dataset warrants. Further, due to the equivocal and inconsistent nature of the cancer response in the rat and mouse studies (in rats, effects seen only in males; in mice, one study showed effects only in males but even these effects were not reproducible), EPA finds that when judged qualitatively the data indicate no greater than a negligible risk of cancer. Additionally, it is noted that the point of departure (1.1 mg/kg/day) selected for deriving the chronic reference dose will adequately account for all chronic effects determined to result from exposure to fluazinam in chronic animal studies, including the equivocal cancer effects.
There was evidence of increased qualitative susceptibility of fetuses to fluazinam in the developmental toxicity study in rats. In this study, increased incidences of facial/palate clefts and other rare deformities in the fetuses were observed in the presence of minimal maternal toxicity. In a developmental neurotoxicity study, decreases in body weight and body weight gain and a delay in completion of balano-preputial separation were observed in pups. These effects were seen in the absence of maternal effects, suggesting increased quantitative susceptibility of the offspring.
Quantitative evidence of increased susceptibility was also observed in a developmental neurotoxicity study in rats. In pups, there were decreases in body weight and body weight gain during lactation, and delayed preputial separation observed at 10 mg/kg/day (NOAEL=2 mg/kg/ day). Although the NOAEL of 2 mg/kg/day is lower than that used for the acute RfD for females 13-49 (7 mg/kg/day), the effects noted in the developmental neurotoxicity study are attributable to multiple doses and are considered postnatal effects. Therefore, the study endpoint is not appropriate either for acute dietary exposures or for use with the population subgroup females 13-49 (with this subgroup the concern is for prenatal exposures). The chronic RfD of 0.011 mg/kg/day is based on a lower NOAEL of 1.1 mg/kg/day and is considered protective of potential developmental effects.
EPA has determined that reliable data show that it would be safe for infants and children to reduce the FQPA safety factor to 1X. |
| April 30, 2007 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2007-0234 |
IR-4.
Petition
for New Tolerances. PPs 6E7137 and PP 6E7139. Proposal
to establish a tolerance for residues of the fungicide fluazinam
in or on food commodities in: ; ; and . IR-4 also proposes
to establish a tolerance for residues of fluazinam
and its metabolite AMGT in or on the following food
commodities:An analytical method using gas chromatography
with electron capture detection (GC-ECD) for the determination
of fluazinam residues on beans (snap, lima, and dry), Brassica
crops (broccoli, cabbage and mustard greens), ginseng and
blueberry has been developed and validated.
| Petition PP 6E7137 for
residues of fluazinam |
PPM |
Vegetable, legume, edible podded,
subgroup 6A, except pea
This subgroup includes
14 commodities.
bean, moth • bean, runner • bean, snap
• bean, wax • bean, yardlong • jackbean
• longbean, chinese • pea, dwarf •
pea, edible podded • pea, pigeon • pea,
snow • pea, sugar snap • soybean immature
seed • swordbean
|
0.15 |
Brassica, head and stem, subgroup
5A
This subgroup includes
10 commodities.
broccoli • broccoli, cavalo • broccoli,
chinese • brussels sprout • cabbage •
cabbage, chinese mustard • cabbage, chinese
napa • cauliflower • cavalo broccolo •
kohlrabi
|
0.01 |
Brassica, leafy greens, subgroup
5B
This subgroup includes
8 commodities.
broccoli raab • cabbage, chinese bok choy •
collards • kale • mizuna • mustard
greens • mustard spinach • rape greens
|
0.02 |
| turnip, tops |
0.02 |
| Petition
PP 6E7137 for residues of fluazinam and
its metabolite AMGT |
Bushberry subgroup
13B
This subgroup includes
5 commodities.
blueberry • currant • elderberry •
gooseberry • huckleberry
|
4.5 |
| berry, aronia |
4.5 |
| blueberry, lowbush |
4.5 |
| currant, buffalo |
4.5 |
| guava, chilean |
4.5 |
| barberry, European |
4.5 |
| cranberry, highbush |
4.5 |
| honeysuckle |
4.5 |
| jostaberry |
4.5 |
| Juneberry |
4.5 |
| lingonberry |
4.5 |
| currant, native |
4.5 |
| salal |
4.5 |
| buckthorn, sea |
4.5 |
| Petition
PP 6E7139 for residues of fluazinam |
| Ginseng |
3.0 |
| bean, dry |
0.01 |
Pea and bean,
succulent shelled, subgroup 6B,
except pea
This subgroup includes
10 commodities.
bean, broad succulent • bean, lima succulent
• cowpea • cowpea seed • pea, blackeyed
• pea, english • pea, garden • pea,
green • pea, pigeon • pea, southern
|
0.02 |
|
| April
18, 2002 |
OPP-2002-0003 |
ISK
-
Establishment of an
import tolerance for residues of fluazinam and its metabolite
in or on wine grapes at 3.0 ppm. FINAL RULE.
- 90-day
oral toxicity rats: increased
liver weights and liver
histopathology in males, and increased
lung and uterus weights
in females.
- 90-day
oral toxiciity dogs: retinal
effects, increased relative liver
weight, liver histopathology
and possible increased serum alkaline
phosphatase in females and possible marginal vacuolation
of the cerebral white matter (equivocal).
- 21-Dermal
toxicity rats: increased AST and cholesterol
levels in clinical chemistry determinations (males)...
erythema, acanthosis, and dermatitis.
- Prenatal
developmental toxicity rats: increased facial/
cleft palates, diaphragmatic
hernia, and delayed ossification in
several bone types, greenish amniotic fluid and possible
increased late resorptions and postimplantation loss.
- Prenatal
developmental toxicity rabbits: increased
liver histopathology...
possible
fetal skeletal abnormalities.
- Reproductive
and Fertility effects rats: liver
pathology in F1
males.
- Chronic
toxicity rats: increased testicular
atrophy in males
- Chronic
toxicity dogs: gastric
lymphoid hyperplasia in both sexes
- Carcinogenicitty
mice: Clear evidence of carcinogenicity
(hepatocellular tumors) in male mice, but not in females.
- Combined
chronic toxicity/carcinogenicity rats: liver
toxicity in both sexes, pancreatic
exocrine atrophy in females and testicular
atrophy in males. Some evidence
of carcinogenicity (thyroid gland follicular cell tumors)
in male rats, but not in females.
- Metabolism
and pharmacokinetics rats: considerable
enterohepatic circulation.
According to Stedman's medical dictionary: circulation
such as bile salts which are absorbed from the intestine
and carried to the liver where they are secreted into the
bile and again enter the intestine.
- Special
Study, 4-Week dietary (range-finding) rats: increased serum
phospholipids, increased total cholesterol,
increased relative liver weights, and liver histopathology.
- Special
Study, 4-Week dietary (range-finding)
mice: increased serum glucose,
increased kidney weights.
- Special
Study, 4-Week dietary (range-finding)
mice: vacuolation of white matter
in brain, increased liver weights,
histopathology in liver.
- Special
Study, 90-Day (Special liver study) rats: increased
relative liver weights and
liver histopathology.
- Special
Study,
7-Day inhalation toxicity rats with
Frowncide WP: increased testes
weight (males) and increased liver
weight (females).
- 8
Special mechanistic studies to assess the CNS white matter
vaculation: White matter vaculation in
the CNS of mice, rats and dogs was found to be due to Impurity
5.
|
| Nov
14, 2001 |
OPP-181082 |
4
Pesticide Emergency Exemptions. EPA authorized use on
peanuts to control Sclerotinia blight in:
-- North
Carolina: May 17, 2001 to Oct 1, 2001.
-- Oklahoma: July 15, 2001 to
Oct 15, 2001.
-- Texas: June 1, 2001 to May
31, 2002.
-- Virginia:
June 15, 2001 to Oct 1, 2001. |
| Sept
7, 2001 |
OPP-301160 |
ISK
- request
for Pesticide Tolerances for residues in or on peanuts and
potatoes at 0.02 ppm approved. - FINAL RULE. |
| Dec
20, 2000 |
OPP-181078 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions. 4 Denials, 2 Approvals:
-- North
Carolina: On 5/1/00 EPA denied a request from the NC
Dept. of Agriculture for the use of fluazinam on peanuts to
control Sclerotinia blight. This request was denied based
upon the Agency's inability, at this time, to reach a ``reasonable
certainty of no harm'' finding regarding health effects which
may result if this use were to occur.
-- Oklahoma:
On 5/1/00 EPA denied a request from OK Dept. of Agriculture
for the use of fluazinam on peanuts to control Sclerotinia
blight. This request was denied based upon the Agency's inability,
at this time, to reach a ``reasonable certainty of no harm''
finding regarding health effects which may result if this
use were to occur.
-- Oklahoma:
EPA authorized the use of fluazinam on peanuts to control
Sclerotinia blight; 9/11/00 to 10/15/00.
-- Texas:
On 5/1/00 EPA denied a request from the TX Dept. of Agriculture
for the use of fluazinam on peanuts to control Sclerotinia
blight. This request was denied based upon the Agency's inability,
at this time, to reach a ``reasonable certainty of no harm''
finding regarding health effects which may result if this
use were to occur.
-- Texas:
EPA authorized the use of fluazinam on peanuts to control
Sclerotinia blight; 9/11/00 to 10/1/00.
-- Virginia:
On 5/1/00 EPA denied a request from the VA Dept. of Agriculture
and Consumer Services for the use of fluazinam on peanuts
to control Sclerotinia blight. This request was denied based
upon the Agency's inability, at this time, to reach a ``reasonable
certainty of no harm'' finding regarding health effects which
may result if this use were to occur. |
|
Dec 6, 2000 |
PF-983 |
ISK
- Petition to
Extend Pesticide Tolerances on potato and peanut at 0.02 ppm
and wine grapes at 3.0 ppm. |
| March
15, 2000 |
OPP-181075 |
Application
for Emergency Exemption for use on peanut. US EPA has received
a specific exemption request from the Virginia Department of
Agriculture and Consumer Services and the Oklahoma Department
of Agriculture to use the pesticide fluazinam to treat up to
45,000 acres in Virginia and 33,000 acres in Oklahoma of peanuts
to control sclerotinia blight. |
|