|
Return to
Adverse
Effect
Abstracts
ACTIVITY:
Herbicide (triazolone)
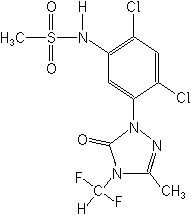
CAS Name:
N-[2,4-dichloro-5-[4-(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-3-methyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]phenyl]methanesulfonamide
Structure:
| Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Endocrine: Prostate
Endocrine: Testicular
Endocrine: Vaginal
Liver
Spleen |
| Environmental
Effects:
•
Persistent in soils
•
Groundwater
Contaminant
•
Highly
Toxic to Estuarine/Marine Organisms
•
Phototoxic
|
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
Yes |
| US
EPA PC Code: |
129081 |
| US
Tolerances: |
CFR
180.498 |
Registered
use in
(includes only a limited list of countries)
|
South
Africa, US |
US
Maximum Residue Levels permitted
in food commodities
|
Permitted
in or on 51 food commodities, including:
Bean -Lima, Chickpea -seed, Cowpeas, Grain
- cereal, Horseradish, Pea - dry,
Soybean seed, Strawberry,
Sugarcane -cane, Sunflower seeds |
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
C11H10Cl2
F2 N4O3S |
| Entry
Year: |
1991 |
| Inventing
Company: |
FMC |
| Manufacturers: |
FMC |
| Other
Names: |
Spartan
Authority
Boral
Capaz
F 6285
FMC 97285 |
| Of
special interest: |
| PAN
Data |
| Material
Safety Data Sheets & Labels |
| January
13, 2006: Summary of
toxicology data: Sulfentrazone (F2685). California EPA.
Department of Pesticide Regulation. Medical Toxicology Branch. |
| February
27, 1997 - US
EPA FACT SHEET |
| March
7, 2001 -
Phototoxic Pesticides:
US EPA Memo Requesting Phototoxicity Study Protocol for Light-Dependent
Peroxidizing Herbicides |
| Undated
- Article:
Evaluation of Herbicides for Nutsedge control in Carrots;
by Kai Umeda. Sulfentrazone was found
"not safe to carrots at the lowest rates tested." |
| May
26, 2000 -
Article: Soybean Injury
from Sulfentrazone - by Aaron Hager
and Christy Sprague. Pest Management and Crop Development Bulletin. |
| April
17, 1998 - Article:
Sulfentrazone-containing Herbicides may cause Soybean Crop Injury.
- Integrated Pest & Crop Management
Newsletter, University of Missouri-Columbia |
Undated
- FMC CORPORATION - Press
Release on Spartan® herbicide
September 1998 - DuPont to market
FMC's sulfentrazone herbicide. - DuPont and FMC have agreed
on specific terms, volumes, and pricing in a product deal that
gives DuPont exclusive marketing rights to sulfentrazone for
use in U.S. soybeans. In the soybean market, sulfentrazone herbicide
has been sold under the brand names, Authority¨ and Canopy XL¨,
and DuPont was already a distributor for the product. FMC will
continue to manufacture sulfentrazone, and to market and sell
the brandnames Spartan¨ for use in U.S. tobacco, and Boral¨
for use in Brazilian sugarcane and soybeans. |
| August
2001 -
IR-4: New
Products/Transitional Solution List - This
list contains brief descriptions of numerous new pest control
materials that have been introduced over the last several years.
Additionally, it contains information on some "older"
crop protection chemicals that are believed to have room for
new uses. This List includes: Sulfentrazone
|
| Abstracts |
| October
2001 - Glossary
of Pesticide Chemicals. A listing
of pesticides subject to analysis of residues in foods and feeds
by the US Food and Drug Administration. |
Major
metabolites:
HMS
(N-(2,4-dichloro-5-(4-
(difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-3-hydroxymethyl-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-
1- yl)phenyl)methanesulfonamide)
DMS
(N-(2,4-dichloro-5-(4- (difluoromethyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-oxo-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-
yl)phenyl)methanesulfonamide |
| US
Federal Register
••
Note: Due to length, the following is a partial list.
Click here
to see full list of FR entries. |
| Published
Date |
Docket
Identification Number |
Details |
| August 25, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0659 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions; Agency Decisions and State and Federal
Agency Crisis Declarations
• Iowa: Specific: EPA authorized
the use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to
control broadleaf weeds; June 25, 2006 to December 15, 2006.
• Michigan: EPA authorized
the use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control
broadleaf weeds; June 25, 2006 to December 15, 2006.
• Wisconsin: Specific: EPA
authorized the use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control common groundsel; June 20, 2006 to December 15, 2006.
|
| June 7, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP- 2006-0387 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions; Agency Decisions and State and Federal Agency Crisis Declarations.
• North Dakota: Specific:
EPA authorized the use of sulfentrazone on flax
to control kochia; March 31, 2006 to June 30, 2006.
• Ohio: Specific: EPA authorized
the use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control common groundsel; June 20, 2006 to December 15, 2006.
• Oregon: Specific: EPA authorized
the use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control broadleaf weeds; March 15, 2006 to February 28, 2007.
• Washington: EPA authorized
the use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control broadleaf weeds; March 15, 2006 to February 28, 2007.
|
| August
31, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0223 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions:
•
Michigan.
EPA authorized the use of sulfentrazone
on strawberries to control
broadleaf weeds; June 25, 2005 to December 15, 2005. Contact:
(Andrew Ertman). |
| August
3, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0201 |
Cancellation
of Pesticides for Non-payment of Year 2005 Registration Maintenance
Fees.
| Section
24(c) Registrations canceled for non-payment of the
2005
maintenance fee are shown in the following Table 1:
Table
1.--Section 24(c) Registrations Canceled for Non-Payment
of Maintenance Fee |
|
SLN no. |
Product
Name |
| 000279
ID-04-0001 |
Spartan
Herbicide |
| 000279
NV-04-0001 |
Spartan
Herbicide |
| 000279
OR-04-0024 |
Spartan
Herbicide |
| 000279
WA-04-0002 |
Spartan
Herbicide |
|
| July
13, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0188 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions:
Oregon: EPA authorized the use
of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control broadleaf weeds; March 11, 2005 to February 28, 2006.
Washington: EPA authorized the
use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control broadleaf weeds; March 2, 2005 to February 28, 2006.
Wisconsin: Specific: EPA authorized
the use of sulfentrazone on strawberries
to control broadleaf weeds; June 20, 2005 to December 15, 2005. |
| March 10,
2005 |
OPP-2005-0057 |
Requests
to Voluntarily Cancel Certain Pesticide Registrations.
Unless a request is withdrawn by September 6, 2005, orders will
be issued canceling these registrations. The Agency will consider
withdrawal requests postmarked no later than September 6, 2005.
| Chemical
Name |
Registration
No. |
Product
Name |
Company
Name and Address |
| Sulfentrazone |
000279
WA-04-0002 |
Spartan
Herbicide |
FMC
Corp. Agricultural Products
Group, 1735 Market St, Philadelph, PA 19103 |
|
| Feb
10, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0025 |
Removal
of Expired Time-limited Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions.
FINAL
RULE.
• 20.
Sulfentrazone. The time-limited tolerance
for chickpea seed is being
removed from Sec. 180.498 because
it expired on December 31, 2004. |
| Dec 10,
2004 |
OPP-2004-0392 |
Extension
of Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions. FINAL
RULE.
EPA has authorized under FIFRA section 18 the use of sulfentrazone
on lima beans and cowpeas for
control of hophornbeam copperleaf in
Tennessee. This regulation extends a time-limited tolerance
for combined residues of the herbicide
sulfentrazone and the metabolites
3-hydroxymethyl sulfentrazone and 3-desmethyl sulfentrazone
in or on succulent bean seed
without pod at 0.1
ppm for an additional 3-year period. This tolerance will expire
and is revoked on December 31, 2007. A time-limited
tolerance was originally published in the Federal
Register of September 21, 1999 (64
FR 51060) (FRL-6097-8).
Note:
This FR of Sept 21, 1999, titled "Sulfentrazone; Pesticide
Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions" stated:
--
Developmental toxicity studies - Rats:
In EPA's oral developmental study in rats, the maternal
(systemic) NOAEL was 25 mg/ kg/day, based on increased relative
spleen weights and splenic extramedullary hematopoiesis
at the LOAEL of 50 mg/kg/day. The
developmental (fetal) NOAEL was 10 mg/kg/day, based on decreased
mean fetal weight and retardation in skeletal development
as evidenced by increased numbers of litters with any variation
and by decreased numbers of caudal vertebral and metacarpal
ossification sites at the LOEL of 25 mg/kg/day.
-- The developmental (fetal) NOAEL
was 100 mg/kg/day, based on decreased
fetal weight and increased fetal variations (hypoplastic
or wavy ribs, incompletely ossified lumbar vertebral arches,
incompletely ossified ischia or pubes, and reduced numbers
of thoracic vertebral and rib ossification sites) at the
LOAEL of 250 mg/kg/day.
-- Reproductive toxicity study --
Rats. In the 2-generation reproductive toxicity study
in rats- The reproductive NOAEL was 14/16 mg/kg/day, based
on: (a) Increased duration of gestation in both F1 and F2
dams; (b) decreased fertility in F1
generation (males); and/or (c) atrophy
of the germinal epithelium of the testes, oligospermia and
intratubular degeneration of the seminal product in the
epididymis at the LOAEL of 33/40 mg/kg/day.
--
Chronic risk. RfD = 0.14 mg/kg/day.
For chronic dietary risk assessment
the Agency recommended use of the NOAEL of 14 mg/kg/day
with an uncertainty factor of 100, based on:
(a)
Decreased maternal body weight and/or body weight gain during
gestation in both P and F1 generations;
(b) reduced premating body
weight gains in the second generation
(F1 adults);
(c) increased duration of gestation
in both F1 and F2 dams;
(d) reduced prenatal viability
(fetal and litter);
(e) reduced litter size;
(f) increased number of stillborn
pups;
(g) reduced pup and litter
postnatal survival;
(h) decreased pup body weights
throughout lactation;
(i) decreased fertility in
F1 generation males; and
(j) atrophy of the germinal
epithelium of the testes, oligospermia and intratubular
degeneration of the seminal product in the epididymis at
the L
|
| Due
to length, the above is a partial list. Click
here to see full list of Federal Register entries. |
|