|
Return to
Adverse
Effects
Abstracts
ACTIVITY:
Fungicide (unclassified)
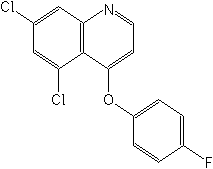
CAS Name:
5,7-dichloro-4-(4-fluorophenoxy)quinoline
Structure:
| Adverse
Effects:
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Brain
Cholesterol
Endocrine:
Pituitary
Endocrine: Testicular
Endocrine: Thymus
Kidney
Liver
|
| Environmental
Effects:
Sweden:
"...
high persistence, high potential for bioaccumulation and indicated
potential for long-range transport. Substances like quinoxyfen
may accumulate in various environmental compartments, including
biota, and the effects of such accumulation are unpredictable..." |
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
Yes |
| US
EPA PC Code: |
055459 |
| US
Tolerances: |
CFR
180.588 |
| California
Chemical Code |
5787 |
Registered
use in
(includes only a limited list of countries)
|
Germany,
Hungary, Portugal, South Africa, UK |
US
Maximum Residue Levels permitted
in food commodities
|
US:
On
Sept 29, 2003, EPA approved the first-time tolerances to be
established for the residues of quinoxyfen
Cherry (sweet & tart), Grape, Hop
(dried cones)
US.
Time-Limited to Dec 2007:
Pumpkin
Squash, winter
Vegetable,
cucurbit, subgroup 9A
(includes 19 commodities) |
UK
Temporary MRL's
|
Strawberries:
0.3 ppm (as of April
2005)
Hops: 1.0 ppm (as of Feb
2005)
|
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
C15H8Cl2
F NO |
| Entry
Year: |
1997
|
| Manufacturers: |
Dow
Agro |
| Other
Names: |
Arius
DE-7956
Elios
Fortress
Legend
Quintec |
| Of
special interest: |
| PAN
Data |
| November
27, 2003 -
Review report for the active substance quinoxyfen. 6781/VI/97-Final.
European Commission. Health & Consumer Protection Directorate-General.
|
| October
4, 2001 -
SUMMARY OF TOXICOLOGY DATA
QUINOXYFEN (XDE-795 & XR-795). California
EPA, Department of Pesticide Regulation, Medical Toxicology
Branch. |
July
20, 2004. New
York Bureau of Pesticides declares crisis and approves the
use of Quintec on pumpkins in Long Island. |
| February
18, 2002 - European
Commission decision to extend provisional authorisation
granted for new active substances: carfentrazone-ethyl,
cinidon-ethyl, cyhalofop-butyl, ethoxysulfuron, famoxadone,
flazasulfuron, flufenacet,
flumioxazine, flurtamone,
fosthiazate, isoxaflutole, metalaxyl-M, prosulfuron, Pseudomonas
chlororaphis, quinoxyfen,
Spodoptera exigua nuclear polyhedrosis virus and sulfosulfuron
|
| 2003
- US
EPA 2003 work plan for registration
of 19 conventional pesticides; 6 of the 19 are fluorinated.
They are Butafenacil,
Flonicamid, Flufenpyr-ethyl, Noviflumuron,
Quinoxyfen, Trifloxysulfuron |
| December
7, 2001: European Commission.
Short report of the meeting
of the Standing Committee on Plant Health held
on 7 December 2001 in Bruxelles. SCPH 5/01. |
| Abstracts |
| February
14, 2001 -
Ingredient in Fortress
Duo Fungicide. Safety Data Sheet. |
| August
2001 - IR-4:
New Products/Transitional
Solution List - This
list contains brief descriptions of numerous new pest control
materials that have been introduced over the last several years.
Additionally, it contains information on some "older"
crop protection chemicals that are believed to have room for
new uses. This List includes: Quinoxyfen |
| October
2001 -
Glossary of Pesticide Chemicals
- A listing of pesticides subject to analysis of residues in
foods and feeds by the US Food and Drug Administration. |
| US
Federal Register |
| Date
Published |
Docket
Identifiction Number |
Details |
| August 25, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0167 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
tolerance. FINAL
RULE.
in or on commodities:
-- Lettuce, head at 7.0 ppm
-- Lettuce, leaf at 19 ppm
-- Pepper, bell at 0.35 ppm
-- Pepper, nonbell at 1.7 ppm
-- Strawberry at 0.90 ppm
-- Melon, subgroup 9A at 0.08
ppm
This subgroup
includes 6 commodities.
cantaloupe • citron melon • melon • melon,
citron • muskmelon • watermelon |
| August 25, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0659 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions; Agency Decisions and State and Federal
Agency Crisis Declarations
• New York: Specific: EPA authorized the use of quinoxyfen
on non-edible cucurbits to control
powdery mildew; July 1, 2006 to September 30, 2006. |
| August
31, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0223 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions:
•
Arizona. Crisis: On May 04, 2005, for
the use of quinoxyfen on watermelons
to
control powdery mildew. This program is expected to end on
September 30, 2005. Contact: (Stacey Groce).
• New York. EPA authorized
the use of quinoxyfen on melons, winter
squash, gourds,
and pumpkin (non-edible cucurbits) to control powdery
mildew; June 30,
2005 to September 30, 2005. Contact: (Stacey Groce) |
| April 21, 2006 |
EPA-HQ-OPP-2006-0167 |
IR-4.
Pesticide
petitions: PP 3E6755, PP 5E6969, PP 5E6970.
PP 3E6755
-- eggplant at 1.0 ppm
-- peppers, bell and non-bell at.1.0 ppm;
PP 5E6969
-- Melon (Subgroup 9A) at 0.1 ppm;
This subgroup includes 6 commodities:
cantaloupe • citron melon • melon •
melon, citron • muskmelon • watermelon
PP 5E6970
-- Lettuce, head and leaf at 17.0 ppm
-- strawberry at.0.8 ppm. |
| Jan
28, 2005 |
OPP-2005-0009 |
Pesticide
Tolerances for Emergency Exemptions for New York State.
FINAL
RULE. EPA,
on its own initiative,
in accordance with sections 408(e) and 408 (l)(6) of the Federal
Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FFDCA), 21 U.S.C. 346a, is establishing
the following tolerances for residues of the fungicide quinoxyfen
in or on
| Commodity
|
Parts
per million |
Expiration/
revocation date |
| Pumpkin |
0.30
|
12/31/07 |
| Squash,
winter |
0.30
|
12/31/07 |
| Vegetable,
cucurbit, subgroup 9A * |
0.30
|
12/31/07 |
*
Vegetable,
cucurbit, group 09 includes:
balsam apple • balsam pear • cantaloupe
• chayote, fruit • cucumber • cucumber,
chinese • cucurbits • gherkin, west indian
• gourd, edible • melon • melon,
citron • muskmelon • pumpkin • squash
• squash, summer • squash, winter •
vegetable, cucurbit, group • watermelon •
waxgourd, chinese
|
The
nature of the toxic effects caused by quinoxyfen are fully
discussed in a Federal
Register Notice published on September 29, 2003 (68 FR
55849) that
established tolerances for residues of quinoxyfen on cherries,
grapes and hops.
Although
this tolerance will expire and is revoked on December 31,
2007, under section 408(l)(5) of the
FFDCA, residues of the pesticide not in excess of the amounts
specified in the tolerance remaining in or on melon subgroup
9A, pumpkin and winter squash after
that date will not be unlawful, provided the pesticide is
applied in a manner that was lawful under FIFRA, and the residues
do not exceed a level that was authorized by this tolerance
at the time of that application. EPA
will take action to revoke this tolerance earlier if any experience
with, scientific data on, or other relevant information on
this pesticide indicate that the residues are not safe.
Because
this tolerance is being approved under emergency conditions,
EPA has not made any decisions about whether quinoxyfen meets
EPA's registration requirements for use on melons, winter
squash, and pumpkins or whether a permanent tolerance for
these uses would be appropriate.
Under these circumstances, EPA does not believe that these
tolerances serve as a basis for registration of quinoxyfen
by a State for special local needs under FIFRA section 24(c).
Nor do these tolerances serve as the basis for any State other
than New York to use this pesticide on these crops under section
18 of FIFRA without following all provisions of EPA's regulations
implementing FIFRA section 18 as identified in 40 CFR part
166 |
| Dec 22,
2004 |
OPP-2004-0350 |
Pesticide
Emergency Exemptions.
--
New YorkDepartment
of Environmental Conservation
Crisis: On July 21, 2004, for the use of quinoxyfen
on cucurbits to control powdery
mildew. This program ended on September 30, 2004. Contact: (Stacey
Groce) |
| Nov
26, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0358 |
3
Pesticide Emergency Exemptions.
-- Idaho Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of quinoxyfen on
hops to control powdery mildew; July 1, 2003 to September
15, 2003. This request was granted because the Agency has determined
that the onset of the powdery mildew pest problem has created
an urgent and non-routine situation which will result in a significant
economic losses for hops growers.
-- Oregon Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of quinoxyfen on hops
to control powdery mildew; June 15, 2003 to September 15, 2003.
This request was granted because the Agency has determined that
the onset of the powdery mildew pest problem has created an
urgent and non-routine situation which will result in a significant
economic losses for hops growers.
-- Washington Department of Agriculture.
EPA authorized the use of quinoxyfen on
hops to control powdery mildew;
July 1, 2003 to September 15, 2003. This request was granted
because the Agency has determined that the onset of the powdery
mildew pest problem has created an urgent and non-routine situation
which will result in a significant economic losses for hops
growers. |
| Sept
29, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0218 |
IR-4.
Pesticide tolerances. FINAL RULE. These
are the first tolerances to be established for the residues
of quinoxyfen by US EPA.
| Commodity |
Final
Rule:
PPM |
May
30:
requested by IR4-:
PPM |
| Cherry,
sweet |
0.30 |
0.4
ppm |
| Cherry,
tart |
| Hop,
dried cones |
3.0
|
5
ppm |
| Grape
|
0.60
|
0.70 |
The
primary target organs affected by quinoxyfen are the liver
and kidney. Liver effects were seen in rat and mouse
subchronic and dog chronic studies. Subchronic effects in
rats and mice included increased liver weights, hepatocellular
hypertrophy and individual cell hepatocellular necrosis. These
effects were noted at high doses and not observed in the chronic
rat and mouse studies since they were performed at lower doses.
Chronic effects in the dog included increased liver weights,
increased alkaline phosphatase levels and increased incidences
of slight microscopic hepatic lesions (increased bile in canaliculi
and increased hepatocyte size). Kidney effects were noted
only in the rat combined chronic/carcinogenicity study which
resulted in an increased severity of chronic progressive glomerulonephropathy
in the males. Rabbits were much more susceptible to the effects
of quinoxyfen than any other species. Systemic effects observed
in the rabbit developmental study included inanition, loss
of body weight, perineal soiling, blood in the cage pan associated
with urine, and abortions. Body weight
decrements were noted in the rat and/or mouse subchronic,
chronic and carcinogenicity studies and the rabbit developmental
and rat reproduction studies. |
| May
30, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0071 |
DOW
AgroSciences; IR-4
- Pesticide Tolerance
Petition; to establish tolerances in or on in or on the
following raw agricultural commodities:
Two Pesticide Petitions:
1E6302: Grape at 0.70 ppm
1E6302: hop, dried at 5 ppm
2E6474: cherry at 0.4 ppm
-- Subchronic
and chronic toxicity. Quinoxyfen caused increased
liver weights and microscopic hepatocellular hypertrophy when
given at sufficiently high dose levels in rats and mice for
13 weeks;
-- increased kidney weights, and
an increase in the incidence of chronic
progressive glomerulonephropathy, were seen after 24
months in female rats given high dose levels of quinoxyfen.
Chronic toxicity seen in dogs included liver
effects as noted above, along with regenerative
anemia at high dose levels. |
| March
26, 2003 |
OPP-2003-0053 |
Application
for Emergency Exemption; Solicitation of Public Comment.
EPA has received specific exemption requests from the Idaho
Department of Agriculture, the Oregon Department of Agriculture,
and the Washington State Department
of Agriculture to use the pesticide quinoxyfen to treat up
to a total of 19,500 acres of hops to control powdery
mildew; 3,000 acres in Idaho, 3,500
acres in Oregon, and 13,000 acres in Washington. The
Applicants propose the use of a new chemical which has not
been registered by EPA. The U.S. is
the second largest producer of hops in the world. The
States estimate that there will be an 8% to 30% loss of gross
revenues without the use of quinoxyfen. No risk information
is provided in this petition. |
|