|
Return to
PROFUME Index page
Adverse Effects Part 1
Adverse Effects Part 2
Abstracts
ACTIVITY: Fluorine
fumigant (Inorganic)
Note: Sulfuryl
fluoride has two uses:
Vikane - for structural fumigation
ProFume - for fumigation of food & feed facilities (click
here)
Structure:
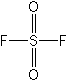
| Adverse
Effects Part 1:
Amyloidosis
- Kidney
Blood
Body Weight Decrease
Bone
Brain
CNS
Deaths from Vikane fumigation
Endocrine: Adrenal
Endocrine: Hypothalmus
Endocrine: Thyroid
Adverse
Effects Part 2:
Eye
Heart
Kidney
Liver
Lung
Tremors/Convulsions |
Regulatory
Information
(only comprehensive for the US) |
| US
EPA Registered: |
Yes |
| US
EPA Product Reg No. |
62719-4 |
| Shipping
numbers |
UN
2191
IMO 2.3 |
| California
Chemical Code |
618 |
Registered
use in
(includes only a limited list of countries)
|
Switzerland,
UK, US |
| Other
Information |
| Molecular
Formula: |
SO2F2
INORGANIC |
| Manufacturers: |
Dow
Agro |
| Other
Names: |
Vikane
Fluoro de sulfurilo (Italian)
Fluorure de sulfuryle (French)
Sulfonyl fluoride
Sulfur difluoride dioxide
Sulfuric oxyfluoride
Sulfuryl fluoride
Sulphuryl difluoride
Termafume (cancelled) |
| Manufacture
sites: |
US:
Dow
Chemical, Pittsburg, California
|
| Of
special interest: |
| PAN
Data. (Bad Actor pesticide: Acute
toxicity) |
Material
Safey Data Sheet & Labels |
CHLOROPICRIN
(the inert used in Vikane) EPA
DOCUMENTS AVAILABLE:
(Note: to view updated documents search the Federal Register
at http://www.regulations.gov/fdmspublic/component/main
|
In
January 2007, California solicited public comments on proposal
to designate sulfuryl fluoride as a toxic air contaminant
(TAC). A public hearing
has been scheduled to receive oral comments regarding the
proposed regulatory changes.
• Comments
submitted by FAN and Beyond Pesticides
(January 31, 2007)
• Proposed
text
• Proposed
Regulatory Action
• Initial
Statement of Reasons
• July 2006: Sulfuryl fluoride (Vikane® ). Health
Risk Assessment.
• July 2006: Sulfuryl fluoride (Vikane® ).
Exposure Assessment.
• July 2006: Sulfuryl fluoride (Vikane® ). Environmental
Fate.
• August 29, 2006: Findings
of the California Scientific Review Panel on the Proposed
Identification of Sulfuryl Fluoride as a Toxic Air Contaminant
• September 2006: Sulfuryl fluoride (Vikane®
) Risk
Characterization Document. Executive Summary
• September 18, 2006: : Statement
of the director of the California Department of Pesticide
Regulation to declare sulfuryl fluoride as a toxic air
contaminant (TAC). The state statute defines TACs as air pollutants
that may cause or contribute to increases in serious illness
or death, or that may pose a present or potential hazard to
human health.
|
Jan
23, 2006: Conservation
Group Moves for Court Order Restricting Use of 66 Pesticides
in Core Red-Legged Frog Habitat.
• Note from FAN:
Chloropicrin was one of the 66 pestcides listed. One of its
uses is as a "Warning Agent (odor)" in Vikane®.
San Francisco, Calif. – The Center for Biological Diversity
(CBD) in a legal motion today asked a U.S. District Court
to protect the threatened California red-legged frog (Rana
aurora draytonii) from 66 of the most toxic and persistent
pesticides authorized for use in California, by creating pesticide-free
buffer zones around the frog’s core habitat and by requiring
consumer hazard warnings so that all Californians may learn
how to protect frogs.
In response to a lawsuit filed by CBD against the U.S. Environmental
Protection Agency (EPA) in April of 2002, the District Court
found in September of 2005 that the EPA violated the Endangered
Species Act (ESA) by registering pesticides for use without
considering how they might impact the continued existence
of the red-legged frog. The motion for “injunctive relief”
delivered today asks the court to protect the frog from pesticides
in or adjacent to aquatic frog habitat designated as core
recovery areas, until the EPA completes a formal consultation
with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) on the impacts
of the pesticides on red-legged frogs, as required under the
ESA... CBD is asking the Court to impose a three-year schedule
for the EPA to determine whether the 66 pesticides may affect
the red-legged frog and to complete formal consultations with
USFWS to ensure the pesticides are not jeopardizing the frog
or contributing to its decline. To minimize harm to frogs
during the consultation process, the motion asks for an injunction
on use of the pesticides around aquatic features and upland
habitats within the frog’s core recovery areas, as designated
by USFWS in the agency’s Recovery Plan for the California
Red-legged Frog. This injunction would also apply buffer areas
for terrestrial and aerial pesticide applications, affecting
approximately 7 percent of the current range of the frog and
less than 1 percent of the area of California. CBD is also
requesting that the EPA conduct monitoring for pesticides
in three of the recovery areas to determine whether the buffers
are effectively protecting the frog, inform pesticide users
about the injunction, and post point-of-sale notifications
warning consumers about harmful effects these pesticides may
have on the frog... |
| Compilation
of news reports |
FINAL
DRAFT Sulfuryl Fluoride (Vikane)
RISK CHARACTERIZATION DOCUMENTS
Department of Pesticide Regulation
California Environmental Protection Agency
Volume
I Health Risk Assessment
- June 1, 2005
Volume
II Exposure Assessment -
June 1, 2005
Volume
III Environmental Fate -
July 5, 2005
Volume
IV DPR Responses to Comments -
June 1, 2005
From
Environmental
Fate - Volume III
...
pages 7-8: A search of the open science
literature produced no citations relevant to the fate of
sulfuryl fluoride in the atmosphere ... Little or
no data on sulfuryl fluoride’s environmental and atmospheric
loss processes are available. There are no experimental
data to confirm that it photolyzes in the troposphere or
reacts with OH radicals, NO3 radicals, or O3. It
is entirely possible that sulfuryl fluoride has a long or
very long atmospheric lifetime and should therefore be considered
a greenhouse gas.
|
May
2005 - Sulfuryl fluoride / Vikane (PT8). Document
III-B6.
Toxicological Studies.
Competent Authority Report. Public version. Rapporteur Member
State: Sweden. |
May
2005 - Sulfuryl fluoride / Vikane (PT8). Document
III-B7.
Ecotoxicological Data for the Biocidal Product.
Competent Authority Report. Public version. Rapporteur Member
State: Sweden. |
May
2005 - Sulfuryl fluoride / Vikane (PT8). Document
III-B8 and B9.
Measures to be adopted to protect man, animals and the environment
and Classification, Packaging and Labelling.
Competent Authority Report. Public version. Rapporteur Member
State: Sweden. |
May
2005 - Sulfuryl fluoride / Vikane (PT8). Document
III-B5.
Intended Uses and Efficacy.
Competent Authority Report. Public version. Rapporteur Member
State: Sweden. |
2005
-
Dow Chemical
Plant Expansion. By
Will Rostov and Catherine Engberg.
This is a short article about a settlement entered into that
allowed Dow to dramatically expand its production of sulfuryl
fluoride to 18 million pounds a year at its facility in Pittsburg,
California. |
| Jan
31, 2005 - California: Clarification
of Vikane label regarding the handling of toothpaste and mouthwash. |
| Jan
21, 2005 - California: Inspection
of structures prior to introduction of Vikane. |
Released
in February 2005:
June
18, 2003. Report
for Air Monitoring Around a Structural Application of Sulfuryl
Fluoride Fall - 2002 . Project No. P-02-004. California
Environmental Protection Agency. Air Resources Board. [see
also the Appendices
to this report]
(page
ii): The sampling procedures used for sulfuryl fluoride
for this study were not valid. The laboratory report states:
"With one exception, all samples with quantifiable
results from the primary collection bed demonstrated quantifiable
breakthrough into the secondary bed. Primary charcoal beds
varied greatly in amount of sulfuryl fluoride collected.
Staff consulted with SKC and NIOSH regarding sample breakthrough.
NIOSH indicated that a sample collection rate of one liter
(Ilpm) may be too high and that the collection rate should
be kept at 0.1 Ipm or less. They did not explain why method
development tubes spiked with sulfuryl fluoride gas did
not show breakthrough when subjected to 1 Ipm sampling conditions
for 24 hours. Because there was primary bed breakthrough,
one might assume that sample may have been lost from breakthrough
of the secondary collection beds."
The
laboratory report does not estimate the extent of the breakthrough.
However, the fact that breakthrough onto the secondary bed
occurred for all samples, even those of relatively short
sampling duration (e.g., 2 hours), indicates that loss of
sulfuryl fluoride was likely significant due to an ineffective
sampling technique. The sample results
presented for sulfuryl fluoride in this report are not valid
due to extensive breakthrough. Additional method development
must be conducted to determine appropriate sampling strategies
before further tests are conducted...
|
| US
EPA Registration Eligibility Decision (RED) |
| TOXNET
profile from Hazardous Substances Data Bank |
| September
1993 -
Sulfuryl Fluoride -
EPA's RED Facts |
| June
2, 2004 - Updated
Summary of Toxicological Data, California EPA |
| August
1, 1986 -
Summary of Toxicological
Data, California
EPA |
January
2002. Revised March 2004. Report:
"Use Information and Air Monitoring
recommendations for the pesticide active ingredients Sulfuryl
Fluoride and Chloropicrin." California Department of
Pesticide Regulation, Environmental Hazards Assessment Program.
...
the annual use for structural fumigations in California
from 1999 to 2002 ranged approximately
1,117,000 to 3,900,000 pounds of sulfuryl fluoride (Table
3) ... in the top 15 counties of use. The majority use of
sulfuryl fluoride occurred in three counties - Los Angeles,
Orange, and San Diego.
|
| 1997
-
Article by Caroline
Cox, Journal of Pesticide Reform 17
(2) 17-20 |
| October
1998 - Structural
Pest Management pesticides. FAN's
compilation of information cited on fluorine and organofluorine
pesticides published in General Pest Management, Category 7A.
A Guide for Commercial Applicators. Prepared by: Carolyn Randall,
MSU Pesticide Education Program. Published by
MSU Pesticide Education
(Michigan State University). MSU
manual number: E-2048. |
| January 5, 2002
- Dow
Chemical planning to invest heavily in upgraded plant. |
| 2000
- "P"
is for Poison. Update on Pesticide Use in California Schools,
by TM Olle. A report by Californians for
Pesticide Reform. |
| April
1993 - Pesticide
Information Profile - Cornell Pesticide
Management Education Program |
| June
1985 - Chemical
Fact Sheet - Cornell Pesticide
Management Education Progra |
| Abstracts |
| Vikane
- structural fumigant |
| Pesticide
Products - partial list |
| 2000
US EPA Toxic Release Inventory - brief
summary |
Sulfuryl
fluoride
EPA
Toxic Release Inventory (TRI)
Facility Air Releases by Year
(Note: TRI statistics on Sulfuryl fluoride began
in 1995. The latest statistics for 2003 were released in 2005.
TRI does not include all industries or sources of air releases.) |
| Facility |
State |
2003 |
2002 |
2001 |
2000 |
1999 |
1998 |
1997 |
1996 |
1995 |
Totals |
3M
CO DECATUR
1400 STATE DOCKS RD,
DECATUR,
MORGAN County |
Alabama |
- |
- |
- |
340,000 |
310,000 |
350,00 |
340,000 |
347,000 |
355,000 |
2,042,000
|
DOW
CHEMICAL CO
901 LOVERIDGE RD,
PITTSBURG,
CONTRA COSTA County |
California |
24,258 |
28,500 |
25,000 |
25,000 |
25,000 |
22,000 |
13,000 |
15,000 |
7 |
177,765 |
3M
CO CORDOVA
22614 RT 84 N,
CORDOVA,
ROCK ISLAND County |
Illinois |
200,000 |
190,000 |
190,000 |
270,000 |
190,000 |
94,000 |
75,000 |
- |
|
1,209,000 |
Totals |
224,258 |
218,500 |
215,000 |
635,000 |
525,000 |
466,000 |
428,000 |
362,000 |
355,007 |
3,428,765 |
"Fumigants
-used
to kill insects, insect eggs, and microorganisms- are
the most acutely toxic pesticides used
in agriculture. Because they are gases, fumigants are
usually taken directly into the lungs, where they readily
enter the blood and are distributed throughout the body. Although
inhalation is the most serious source of exposure and can
lead rapidly to death, absorption of fumigants through the
skin can also be a significant hazard
(103) [page 293]."
Ref: U.S. Congress, Office of Technology
Assessment, Neurotoxicity: Identifying and Controlling Poisons
of the Nervous System, OTA-BA-436 (Washington, DC: U.S. Government
Printing Office, April 1990).
http://www.wws.princeton.edu/cgi-bin/byteserv.prl/~ota/disk2/1990/9031/9031.PDF
|
Rationale
for US EPA to add Sulfuryl Fluoride to the Toxic Release
Inventory
The
primary effects of sulfuryl fluoride in humans are respiratory
irritation and central nervous system depression, followed
by excitation and possibly convulsions. Rabbits exposed
via inhalation (6 hours/day, 5 days/week, for 2 weeks) to
sulfuryl fluoride showed hyperactivity, convulsions and
vacuolation of the cerebrum at 600 ppm (2.5 mg/L). Renal
lesions were present in all rats exposed by inhalation (6
hours/day, 5 days/week, for 2 weeks) to 600 ppm (2.5 mg/
L) sulfuryl fluoride. Minimal renal changes were noted in
rats exposed to 300 ppm (1252 mg/L), whereas no effects
occurred at 100 ppm (4.2 mg/ L). Convulsions at near lethal
concentrations were reported in rabbits, mice, and rats.
In a 30-day inhalation study, loss of control, tremors of
the hind quarters, and histopathological changes in the
lung, liver, and kidney were reported in rabbits exposed
to 400 ppm (1.6 mg/L) for 7 hours/day, 5 days/week for 5
weeks. The NOEL was 200 ppm (0.83 mg/L). Cerebral vacuolation
and/or malacia and inflammation of nasal tissues were observed
in rabbits exposed by inhalation to 100 or 300 ppm (0.4
or 1.25 mg/L) for 13 weeks. The NOEL was 30 ppm (0.125 mg/L).
Rats exposed by inhalation to 100 to 600 ppm (0.4 to 0.25
mg/L) sulfuryl fluoride for 13 weeks developed mottled teeth
(indicative of fluoride toxicity), renal and respiratory
effects, and cerebral vacuolation. EPA believes that there
is sufficient evidence for listing sulfuryl fluoride on
EPCRA section 313 pursuant to EPCRA section 313(d)(2)(B)
based on the available neurological, renal, and respiratory
toxicity data for this chemical.
Ref:
USEPA/OPP. Support Document for the Addition of Chemicals
from Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, Rodenticide Act (FIFRA)
Active Ingredients to EPCRA Section 313. U. S. Environmental
Protection Agency, Washington, DC (1993).
As cited by US EPA in:
Federal
Register: January 12, 1994. Part
IV. 40 CFR Part 372. Addition of Certain Chemicals; Toxic
Chemical Release Reporting; Community Right-to-Know; Proposed
Rule.
|
Registered
Uses in the U.S. for Vikane
Uses
Poison, single dose, Insecticide, Miticide
Pests
Drywood termites, Formosan termite, Powderpost beetles,
Furniture beetle, Deathwatch beetle, Old house borer, Carpet
beetle (larvae), Bed bug, Clothes moths, Cockroaches, Rodents
Locations
Domestic dwellings (indoor) (fumigation), Household contents
(stored clothes) (fumigation), Household contents (upholstered
furniture) (fumigation), Terrestrial structures (nonsoil
contact fumigation treatment), Buses (nonfeed/nonfood) (fumigation),
Ships (surface) (nonfeed/nonfood) (fumigation), Railroad
boxcars (nonfeed/nonfood) (fumigation), Trucks (nonfeed/nonfood)
(fumigation), Recreational vehicles (nonfeed/nonfood) (fumigation),
Shiping containers (nonfeed/nonfood) (fumigation), Transportation
vehicles (feed/food empty) (fumigation), Warehouses (empty)
(fumigation)
Source:
Pesticide Action Network
|
Sulfuryl fluoride (SO2F2),
also known as VikaneŠ (99.8 percent by weight sulfuryl fluoride
and 0.2 percent inerts), was developed by Dow Chemical in the
late 1950s as a structural fumigant. Vikane® is currentllly
manufactured by DowElanco, which supplies 100 percent of the Vikane®
structural fumigation market. Since first marketed in the US in
1961, it has been used to fumigate more than one million buildings,
including museums, historic landmarks, rare book libraries, government
archives, scientific and medical research laboratories, and food-handling
facilities. Sulfuryl fluoride is used in approximately 85 percent
of all structural fumigations.
Ref: US EPA. http://www.fluorideaction.org/pesticides/sulfuryl.f.vikane.epa.htm
|