PFOA and PFOS
The molecular structures of the principal PFOA and PFOS chemicals.
PFOA |
PFOS |
| PFOA is perfluorooctanoic acid and is sometimes called C8 or C-8. It is a man-made chemical and does not occur naturally in the environment. — Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA or C8) — CAS No: 335-67-1. 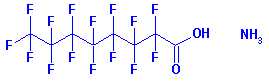 The “PFOA” acronym is used to indicate not only perfluorooctanoic acid itself, but also its principal salts.The PFOA derivative of greatest concern and most wide spread use is the ammonium salt:Ammonium perfluorooctanoate (APFO or C8) The “PFOA” acronym is used to indicate not only perfluorooctanoic acid itself, but also its principal salts.The PFOA derivative of greatest concern and most wide spread use is the ammonium salt:Ammonium perfluorooctanoate (APFO or C8)CAS No. 3825-26-1. Molecular formula: 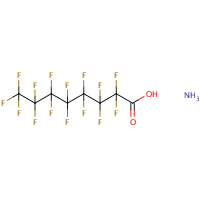
PFOA is used as a processing aid in the manufacture of fluoropolymers to produce hundreds of items such as non-stick surfaces on cookware (TEFLON), protective finishes on carpets (SCOTCHGUARD, STAINMASTER), and clothing (GORE-TEX). The DuPont site where APFO is used as a reaction aid is the Washington Works (Route 892, Washington, West Virginia 26181) located along the Ohio River approximately seven miles southwest of Parkersburg, West Virginia. The Little Hocking Water Association well field is located in Ohio on the north side of the Ohio River immediately across from the Washington Works facility. Consumers of this drinking water have brought a Class Action suit against the Association and DuPont for the contamination of their drinking water with DuPont’s APFO, which residents and media refer to as C8. According to the Environmental Working Group, PFOA is not only used to manufacture Teflon, but is also a breakdown product of chemicals used to coat food packaging, including fast food like McDonald’s, and stain-resistant coatings for couches, carpets, and clothing. PFOA is broadly toxic. It does not break down in the environment, and is considered to be persistent over geologic time scales. It nearly universally pollutes human blood and has a half-life in the body of more than four year |
PFOS is the perfluorooctane sulphonate anion and is not a substance as such. The term PFOS-related substance is used to refer to any or all of the substances which contain the PFOS moiety (defined as the C8F17SO2 group) and may break down in the environment to give PFOS.The parent sulphonic acid and some of its commercially important salts, are:Perfluorooctane sulphonic acid (CAS No. 1763-23-1)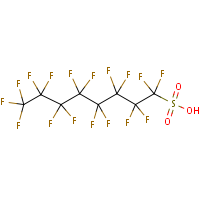 Potassium salt (CAS No. 2795-39-3) Potassium salt (CAS No. 2795-39-3)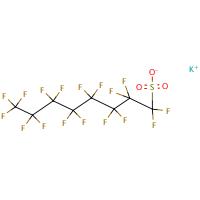 Ammonium salt (CAS No. 29081-56-9) Ammonium salt (CAS No. 29081-56-9)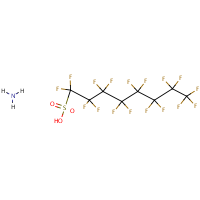 Lithium salt (CAS No. 29457-72-5) 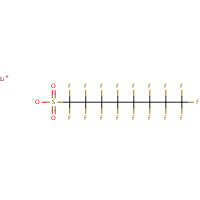 Diethanolamine (DEA) salt (CAS No. 70225-39-5) Diethanolamine (DEA) salt (CAS No. 70225-39-5)— no molecular structure available.The use of products containing these substances can lead to the direct emission of PFOS to the environment.According to a September 2004 UK report — PFOS is: • persistent and bioaccumulative • has been detected in the serum of occupational and general populations • there appears to be an increased risk of episodes for neoplasms of the male reproductive system, the overall category of cancers and benign growths, and neoplasms of the gastrointestinal track. • highly toxic (acute) to honey bees and bioconcentrates in fish • detected in tissues of wild birds and fish, in surface water and sediment, in wastewater treatment plant effluent, sewer sludge and in landfill leachate. |
